Why Isolating Audio Devices May Be a Windows Feature?

Why Isolating Audio Devices May Be a Windows Feature?
Quick Links
- What Is the “Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation” Process?
- Why Does Audiodg.exe Show a High CPU Usage, and Can You Disable It?
- How to Reduce the Resource Consumption of Audiodg.exe
Key Takeaways
- “Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation” is a genuine Windows process that manages audio enhancements and isolates the audio processing.
- High resource consumption by this process could be caused by corrupt audio drivers, excessive sound effects, or third-party audio enhancement apps.
- Reduce resource consumption by updating drivers, tweaking effects, closing extras, and fine-tuning audio settings.
Have you noticed a “Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation” process consuming substantial system resources in the Windows Task Manager? It’s a genuine Windows process responsible for providing a stable audio experience. This guide explains what this process does, why you shouldn’t turn it off, and how you can reduce its resource consumption.
What Is the “Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation” Process?
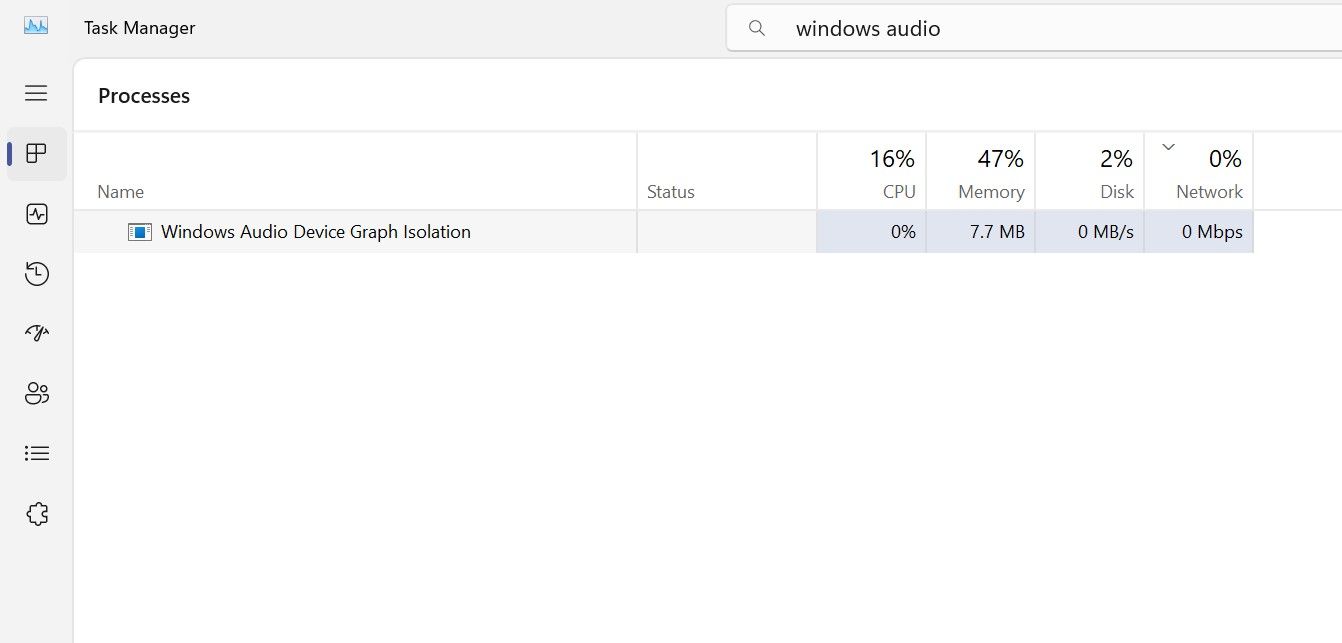
The “Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation” process, referred to as audiodg.exe, is at the core of Windows 11’s audio system.
The process manages audio enhancements and effects applied to the audio output, including equalization, spatial sound, and other audio modifications. Under the hood, it processes sound data and manages the network of connected audio components, like your sound card, drivers, and playback device.
The service is kept isolated from the standard Windows audio service. This “sandboxing” allows third-party audio manufacturers to include their sound enhancement settings (for instance, equalizer effects) without affecting the Windows audio service. Any error doesn’t crash Windows if a particular audio application, driver, or process malfunctions.
Thus, the intentional “sandboxing” provides a more responsive and reliable audio experience. But why does audiodg.exe sometimes consume extensive system resources?
Why Does Audiodg.exe Show a High CPU Usage, and Can You Disable It?
The process typically uses a minimal percentage of the CPU and operates efficiently. Its resource usage can increase if you apply too many sound effects, a third-party audio software consumes resources to deliver high-quality sound, or the audio drivers get corrupted.
This leads to the question: can you turn off this process if the resource usage gets too high? No, this process is an integral part of Windows’ audio system. Disabling it causes audio problems and errors. We turned off this process, played a YouTube video afterward, and encountered the “Audio renderer error. Please restart your computer” error.
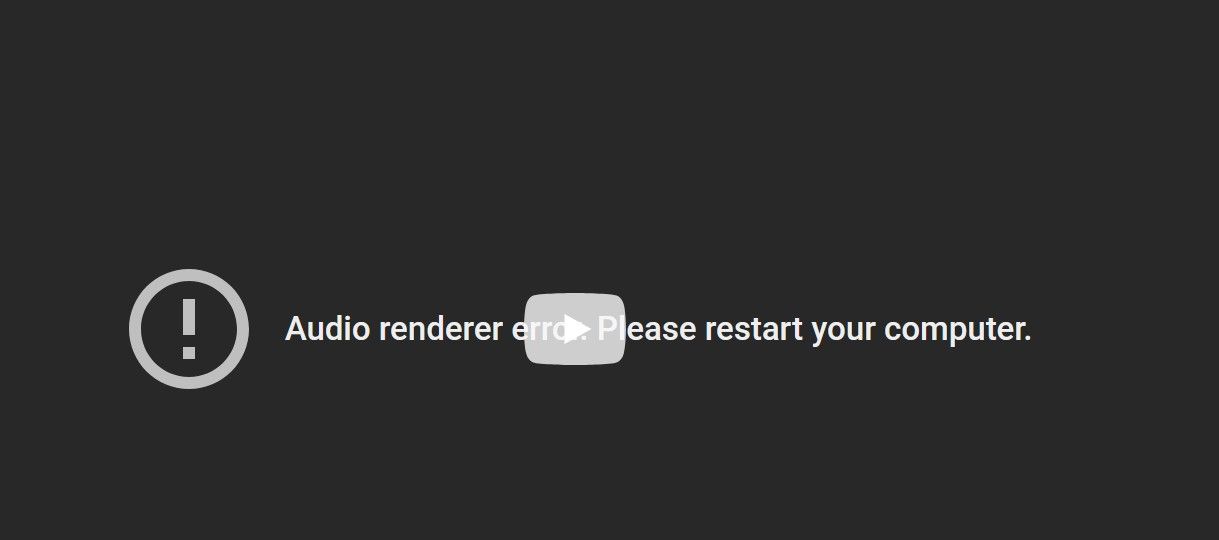
So, if you don’t want to run into audio problems, don’t turn off this process—you won’t hear any sound. Instead, adjust the audio settings to make it use fewer resources. As a core service, you should never terminate it like other vital Task Manager processes.
How to Reduce the Resource Consumption of Audiodg.exe
As this process is notorious for its high resource consumption, malicious programs can disguise themselves as audiodg.exe and exploit your system resources. So, you should first verify that the resource-consuming process in the Task Manager isn’t any malware . If the process turns out to be malicious, you should run a Windows Defender scan to remove it.
If it’s a genuine Windows process, here are some ways to reduce its resource usage:
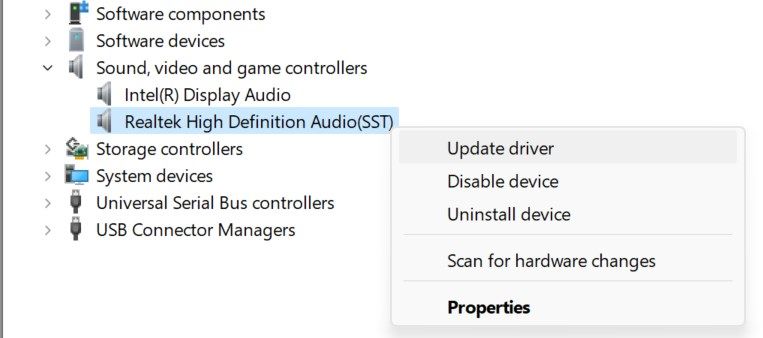
- Ensure you have the latest audio drivers installed. Download the latest audio driver from the manufacturer’s website. If it comes in an executable format, click on the file to install it automatically. If a manual installation is required, right-click the Start button and open Device Manager. Then, expand the Sound, video, and game controllers tab, right-click on the relevant driver, and select Update driver.

Then, click Browse my computer for drivers, locate and select the downloaded driver, and Windows will install it.
- Adjust the default audio format in the sound settings. Press Win+R, type “ms-settings:sound,“ and click OK. After that, scroll down and click More sound settings.

Then, go to the Playback tab, right-click your default audio output device, and select Properties. Then, go to the Advanced tab and select a different sample rate and bit depth from the dropdown menu.
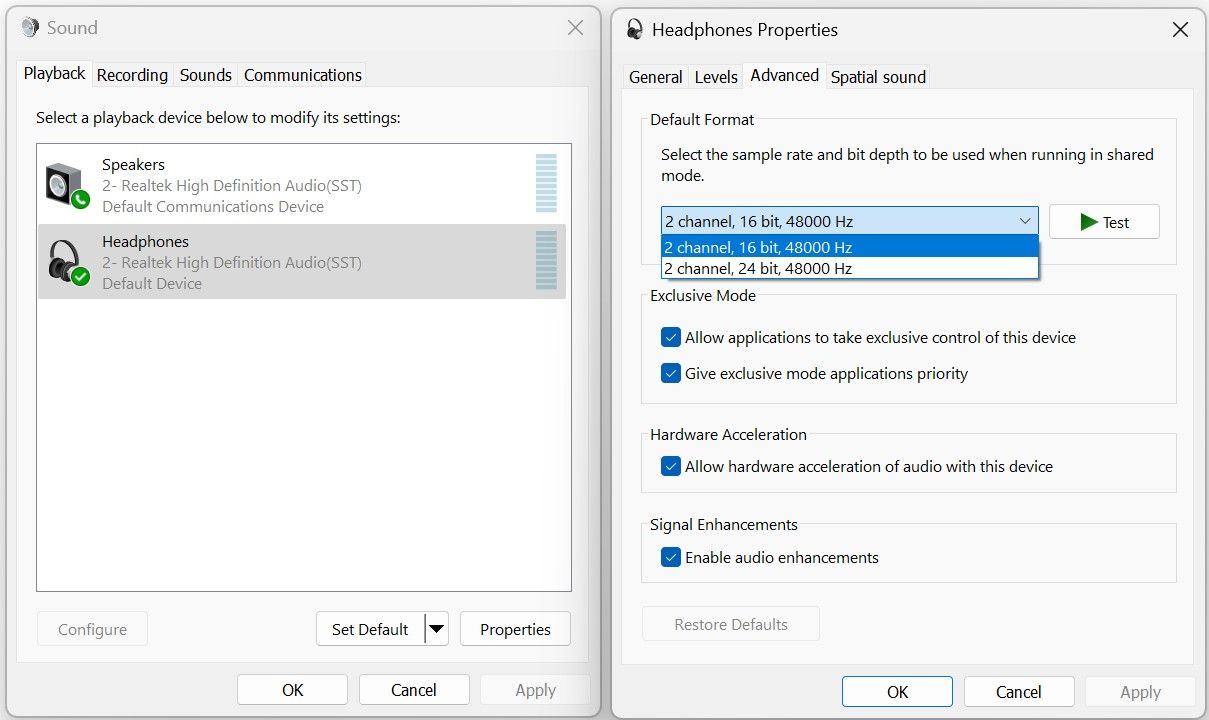
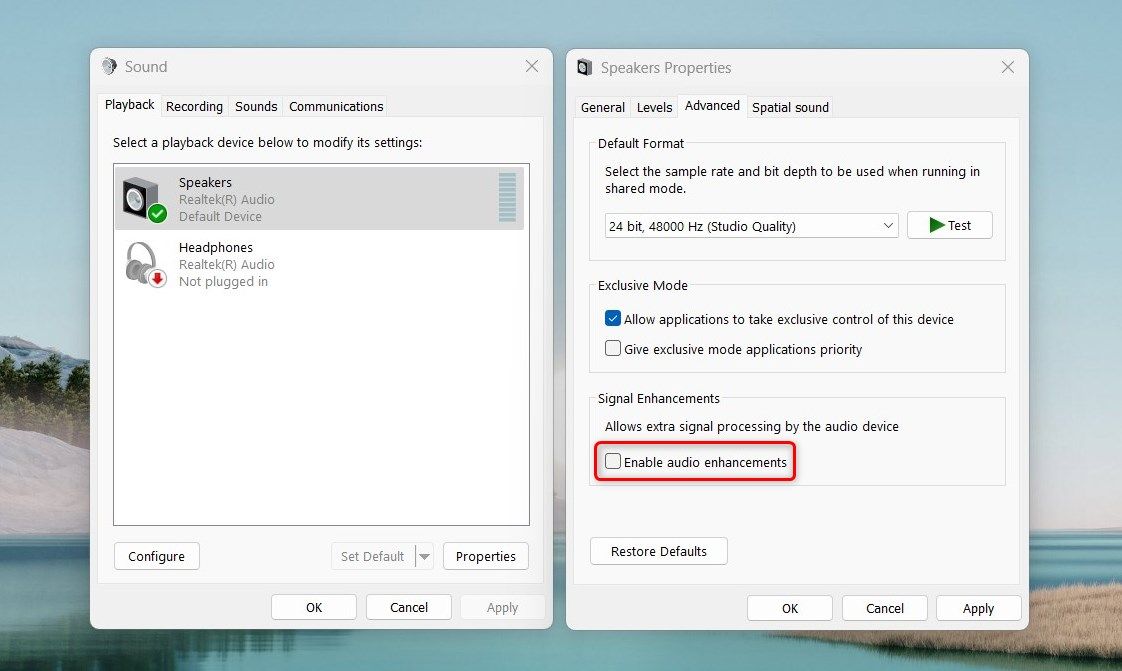
- Disable audio enhancements. Head to the Playback tab, right-click on your audio output device, and select Properties. Then, go to the Advanced tab and uncheck the box beside Enable audio enhancements.
- If you use a third-party app to apply advanced sound effects, stop using it temporarily or deactivate some of its features.
- If the process uses too many resources only when playing audio through a particular app, that app could be the culprit. So, either update or re-install the app or switch to another one.
- Check for pending Windows updates and install them if they are available. Also, check optional driver updates from your audio output device manufacturer and install them.
- If resource usage spikes only when you connect a particular audio output device to your computer, the hardware could be faulty. So, examine it for defects.
In most cases, turning off some sound effects and updating the audio drivers reduces resource consumption of the “Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation” process. Still, it would be best to double-check the process’s authenticity to ensure your device isn’t infected.
Also read:
- [Updated] In 2024, Painless Audio Progression The Unobtrusive Way
- [Updated] In 2024, Virtual Upgrade Social Story Snipper
- [Updated] Legality Check Taking Screencasts of YouTube Videos
- Boosting macOS Usability Through Windows Apps
- Download ASUS ATK0110 ACPI Drivers for Free: Step-by-Step Guide
- Guide to Initiating a Pure Boot in Windows 11
- Hassle-Free Ways to Remove FRP Lock from Samsung Phones with/without a PC
- How to Configure a Windows Hello Fingerprint Login on Windows 11
- How to Reset Apple ID and Apple Password From iPhone X
- In 2024, Craft a Compelling Metaverse Presence with These Tools
- Innovative Ways to Erase TaskView on Bar
- Overcoming Windows Restrictions for Hidden Software
- Proper Techniques for Auditory & Visual Recordings Using the Snipping Tool in Windows 11 (Max 156)
- Resolve Setup Woes: MS PC Manager Fix
- Tackling ONEDRIVE Error Code X04Dec5 on Windows 11 Login
- Unearthing Origin of Mysterious DX Misstep in LOL
- Unveiling Blackout Glitches in Windows Remote Services
- Title: Why Isolating Audio Devices May Be a Windows Feature?
- Author: David
- Created at : 2025-01-08 02:59:33
- Updated at : 2025-01-13 05:12:32
- Link: https://win11.techidaily.com/why-isolating-audio-devices-may-be-a-windows-feature/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.