
The Ultimate Guide to Tracking Disk Space Usage in Windows PCs

The Ultimate Guide to Tracking Disk Space Usage in Windows PCs
Does your device run out of memory frequently? Do you often scratch your head, wondering what is taking up all that space on your drive but can’t figure out what it is? It’s nothing out of the ordinary; every Windows user faces the issue of insufficient disk space sooner or later.
Thanks to Microsoft, finding the apps, documents, and files taking up most of your disk space on Windows and cleaning that space by removing extraneous clutter is now easier than ever. If that’s your goal, read on to find out how to get there.
First, Locate the Overpopulated Disk Drive
Have you partitioned your hard disk into several drives? If you have, check which drive(s) consumes the most space. Do not let the percentage of occupied space fool you; instead, look at the size of the filled territory in GBs. The partition containing more GB of data is more crowded. However, how can you find out which drives are overloaded?
Open Windows File Explorer and click onThis PC . Among all the partitions you’ve created on your drive, identify the ones that contain the most data.
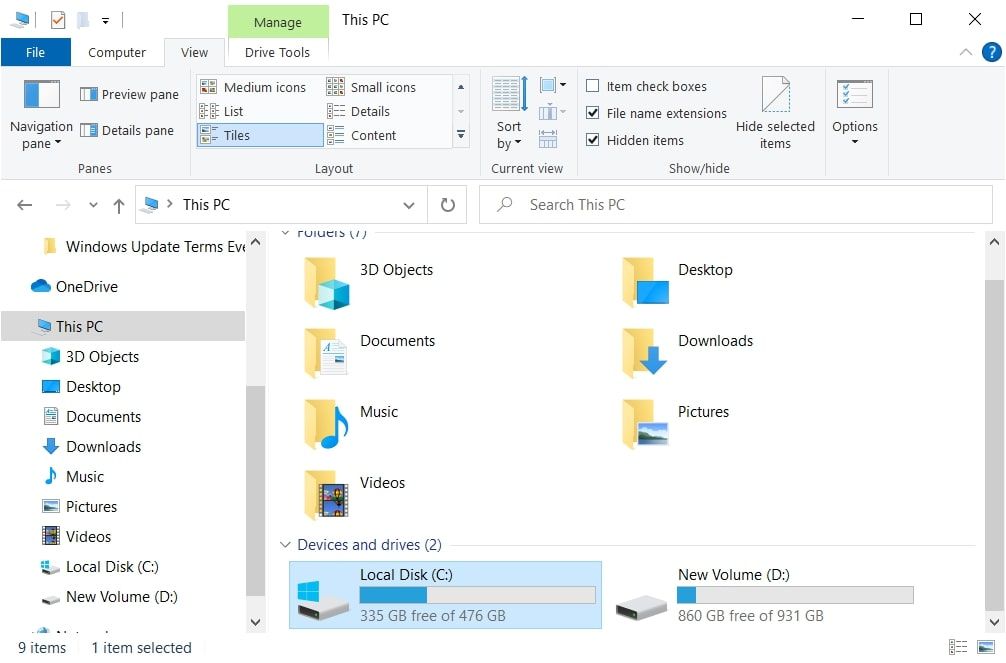
Having found that, let’s look at how to find the data type that occupies the most space.
Identify the Data Type Occupying the Most Space on Your Crowded Drive
Applications and games, system and temporary files, garbage on the desktop, and other data do not take up the same amount of disk space. While some consume hardly any space, others occupy a considerable amount.
Determining which type of data consumes the most space on your drive can help free up space more effectively. Here’s how you can find out:
- Right-click on the WindowsStart button and then clickSettings .
- From the left sidebar, select theSystem tab.
- In the right pane, clickStorage .
- In this section, you can see what type of data occupies the most space on your currently crowded and other drives.
- Click onShow more categories to view other categories that occupy the most real estate.

Ideally, you should start clearing space from the category that consumes the most space on your hard drive. For instance, if apps and features occupy the bulk of your storage, you should free that up first.
How to Free Up Your Windows Storage Drive
Typically, three data types take up most of your drive space: apps and features, system and reserved files, and temporary files. Hence, reducing the burden of these data types can effectively free up your drive space. Let’s see how you can accomplish that.
1. Manage Your Apps and Features
Follow these steps to remove extra apps and features:
- Navigate toSettings > System > Storage .
- Select the drive you wish to free up space on.
- Click onShow more categories .
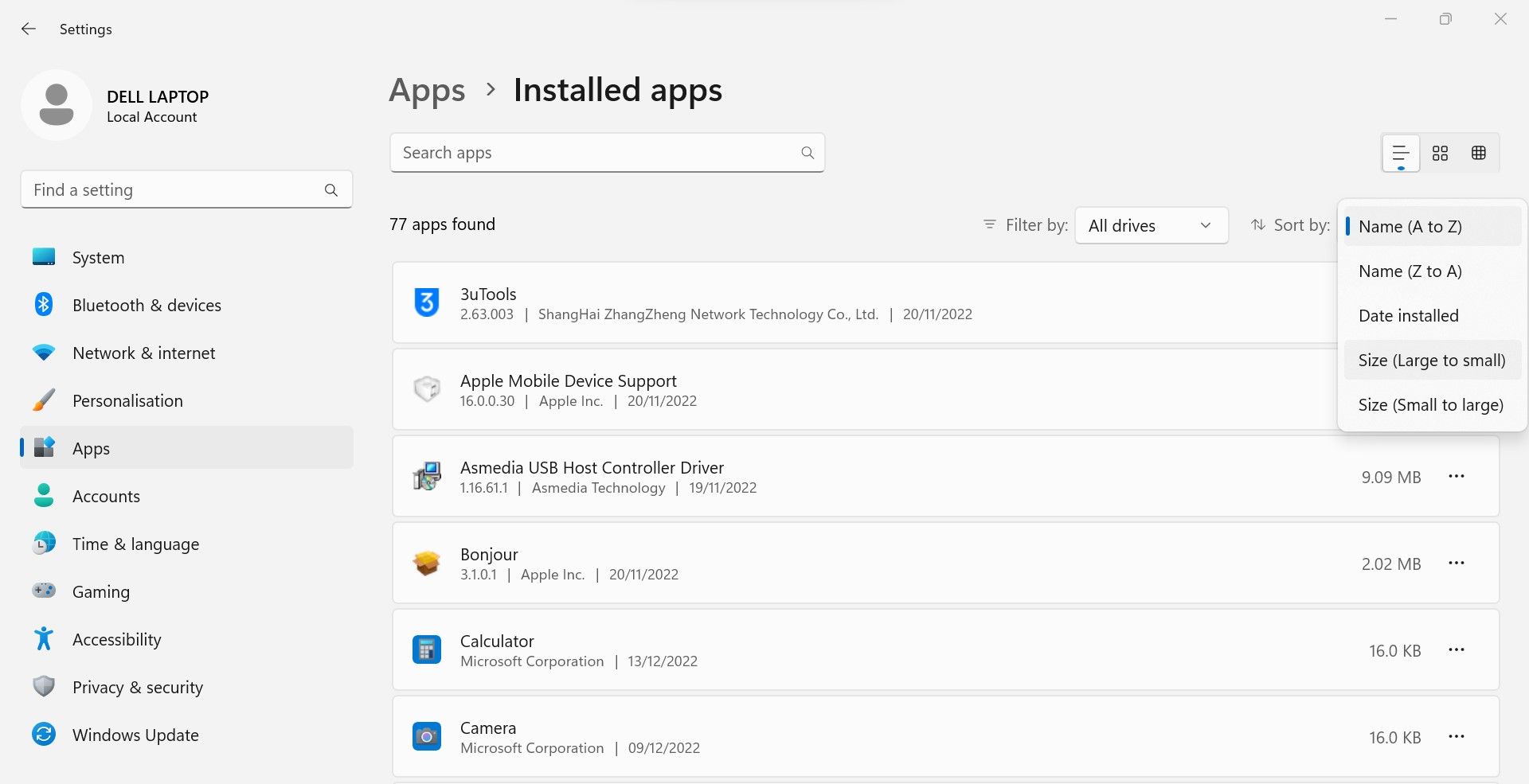
- Then click onApps and Features .
- SelectSize (Large to small) from the dropdown menu next toSort by .

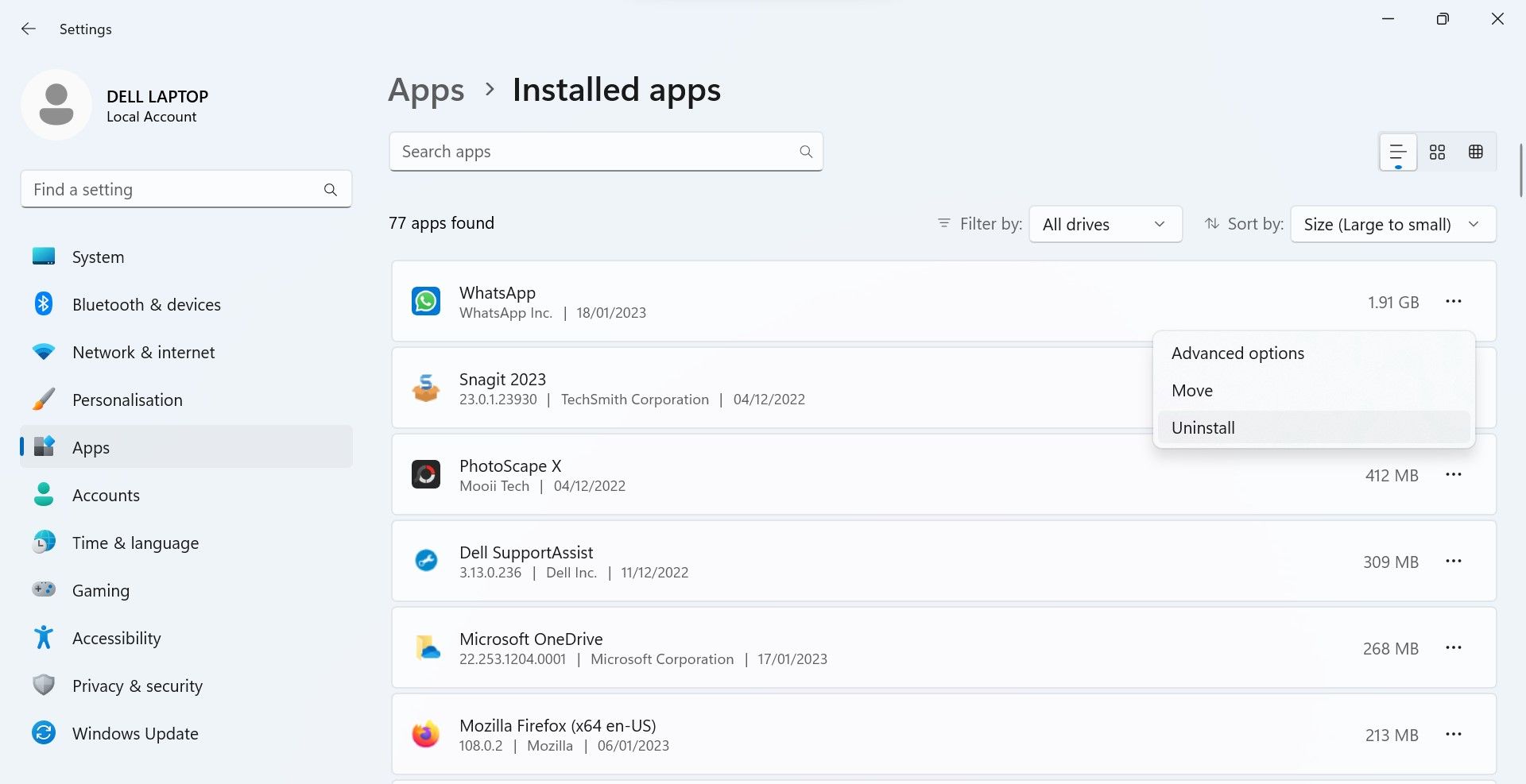
- Determine which apps are redundant and taking up the most disk space.
- Click thethree vertical dots next to each app and clickUninstall .

- Repeat the above step for all apps you find hefty, and you should be able to free up quite a bit of space.
If your operating system lives on the same overcrowded disk, the system and reserved files could be the next big space eater.
2. Manage System and Reserved Files Storage
Be cautious when managing the disk space used by the system and reserved files, as deleting essential files could cause unexpected problems. The overall storage occupied by the system and reserved files is normally divided into five categories: system files, reserved storage, virtual memory, hibernation file, and system restore files.
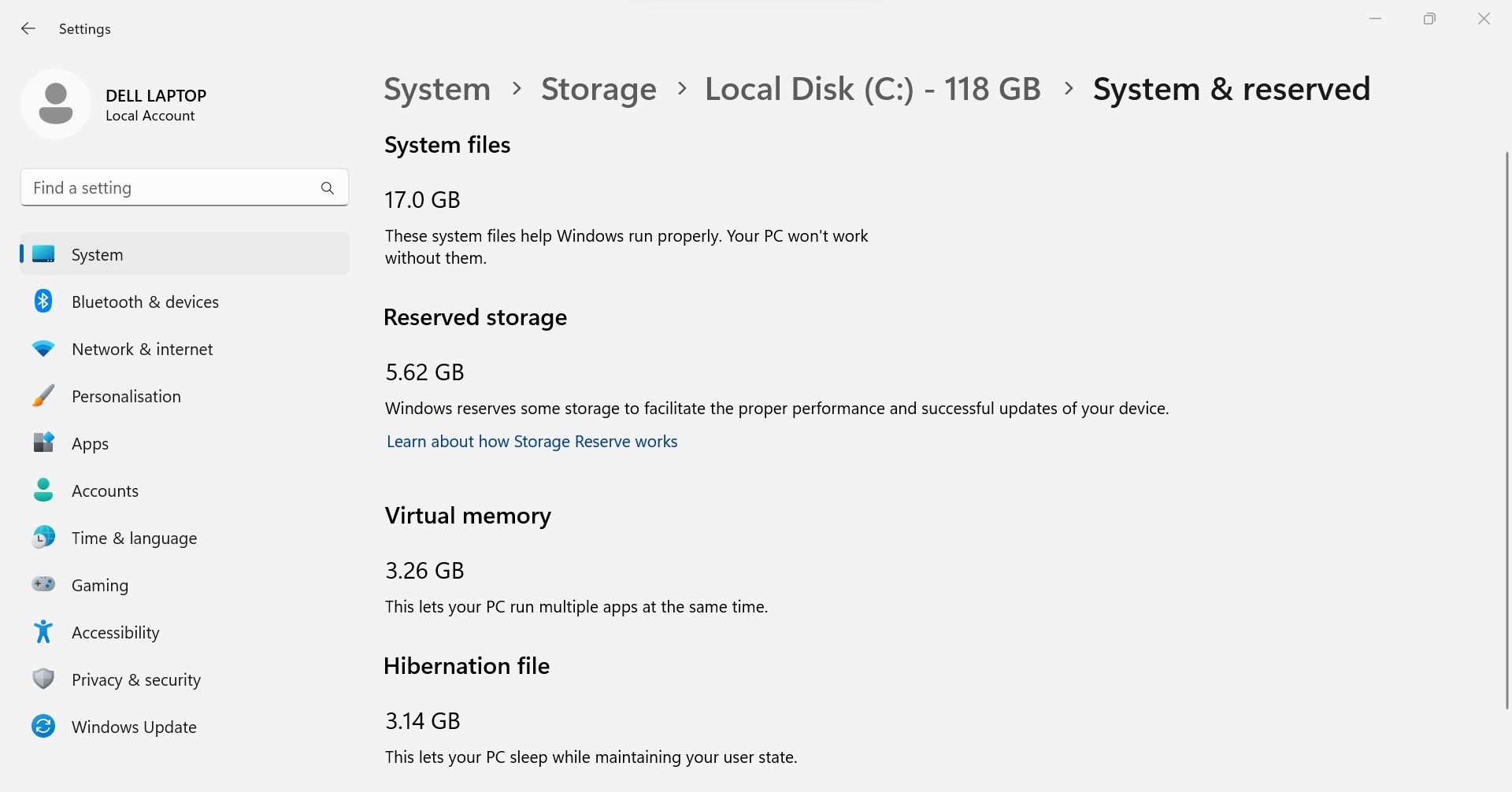
Space consumed by system files, reserved storage, and virtual memory is actually used by your device to perform its functions; refrain from deleting files contained therein. Therefore, there are only two types of storage left to manage; the hibernation file and the space reserved for System Restore. This raises the question: can you free this up?
Although you can disable the hibernation mode, you shouldn’t do so if you frequently use this feature for keeping in-use apps open while the device is in hibernation. However, this feature takes up a lot of space in GBs, so if you aren’t using it, you can free some room. Our guide on if you should delete the Hiberfil.sys file on Windows will walk you through every step.
Likewise, restore points consume a considerable amount of storage, but it is worth it since it allows you to restore your device to a previous point in time if something goes wrong. However, having multiple restore points would be a waste of space on the hard drive. Therefore, it is recommended to delete any extra restore points on Windows you created.
3. Manage Temporary Files Storage
Temporary files usually consume the most space on your drives after system files and installed applications. As their name implies, they are temporary files that only speed up Windows processes. Does that mean you can safely delete them? Yes, but you’ll need to be careful. Here are some tips for clearing temporary files wisely:
- Delete temporary files from theDownloads folder only if you have moved them elsewhere already and all that is left are duplicates.
- DeleteWindows upgrade log files only if you are not experiencing any problems upgrading Windows.
- DeleteThumbnails ,Delivery Optimization Files , andTemporary Internet Files .
- Don’t deleteRecycle Bin data unless you’re confident you won’t need to restore it later.
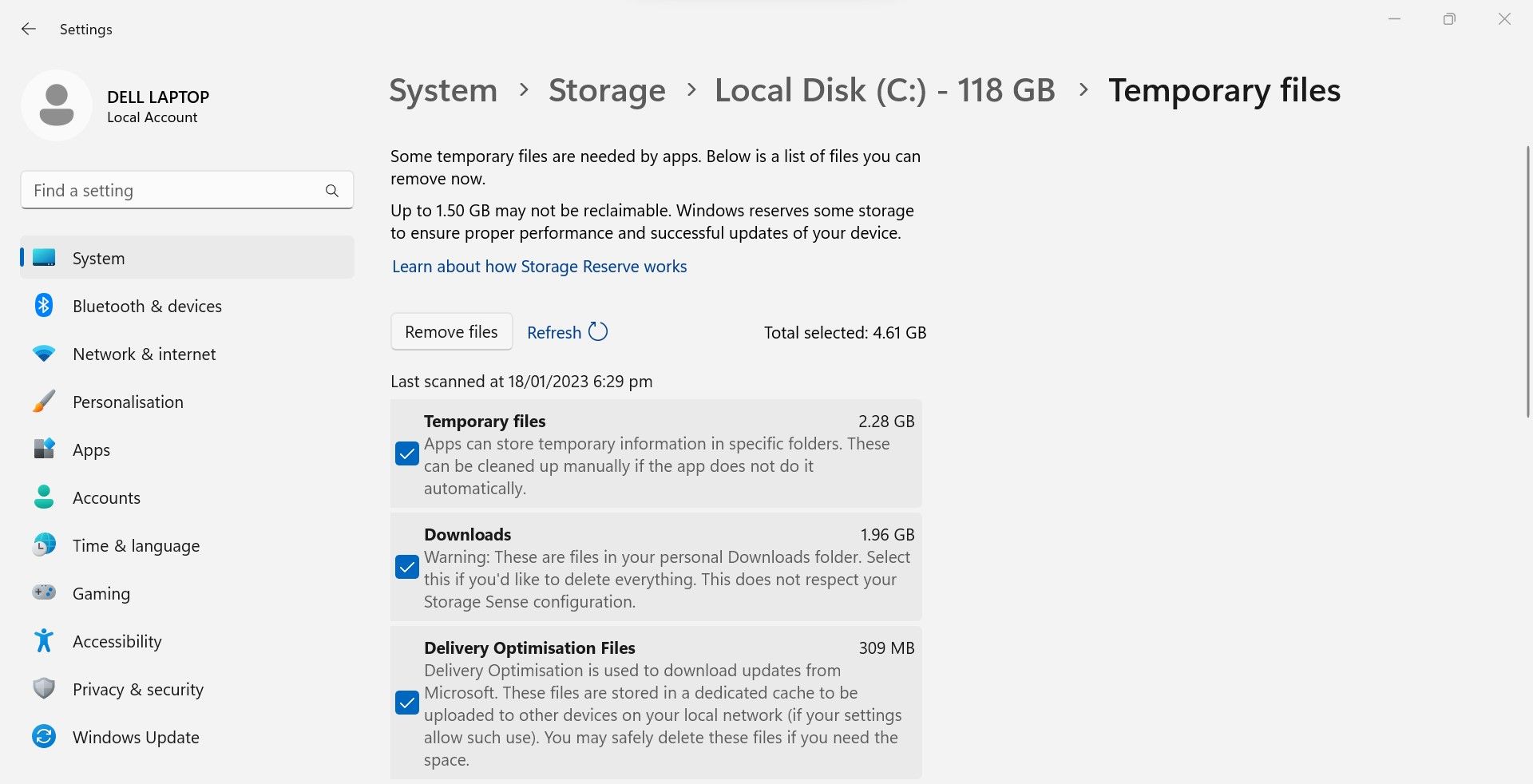
With these tips, you’ll hopefully be able to free up a significant amount of space that was previously unnecessarily occupied. Are you still running low on disk space? If so, then your device’s storage drive is not large enough. So, upgrade it to accommodate your data more effectively.
If you decide to go this route, check out our roundup of best NVMe SSDs for faster performance first.
Avoid Cluttering Up Your Precious Disk Space
Having insufficient disk space and not knowing what’s causing it can be a horrible experience. Hopefully, using the tips in this article, you will be able to identify what apps and files are draining your disk storage the most.
If they are safe to delete, wipe them out. If not, move them to a different drive with more disk space left and relieve some of the pressure from an overfilled drive.
- Title: The Ultimate Guide to Tracking Disk Space Usage in Windows PCs
- Author: David
- Created at : 2024-08-16 00:26:50
- Updated at : 2024-08-17 00:26:50
- Link: https://win11.techidaily.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-tracking-disk-space-usage-in-windows-pcs/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
 PaperScan Professional: PaperScan Scanner Software is a powerful TWAIN & WIA scanning application centered on one idea: making document acquisition an unparalleled easy task for anyone.
PaperScan Professional: PaperScan Scanner Software is a powerful TWAIN & WIA scanning application centered on one idea: making document acquisition an unparalleled easy task for anyone.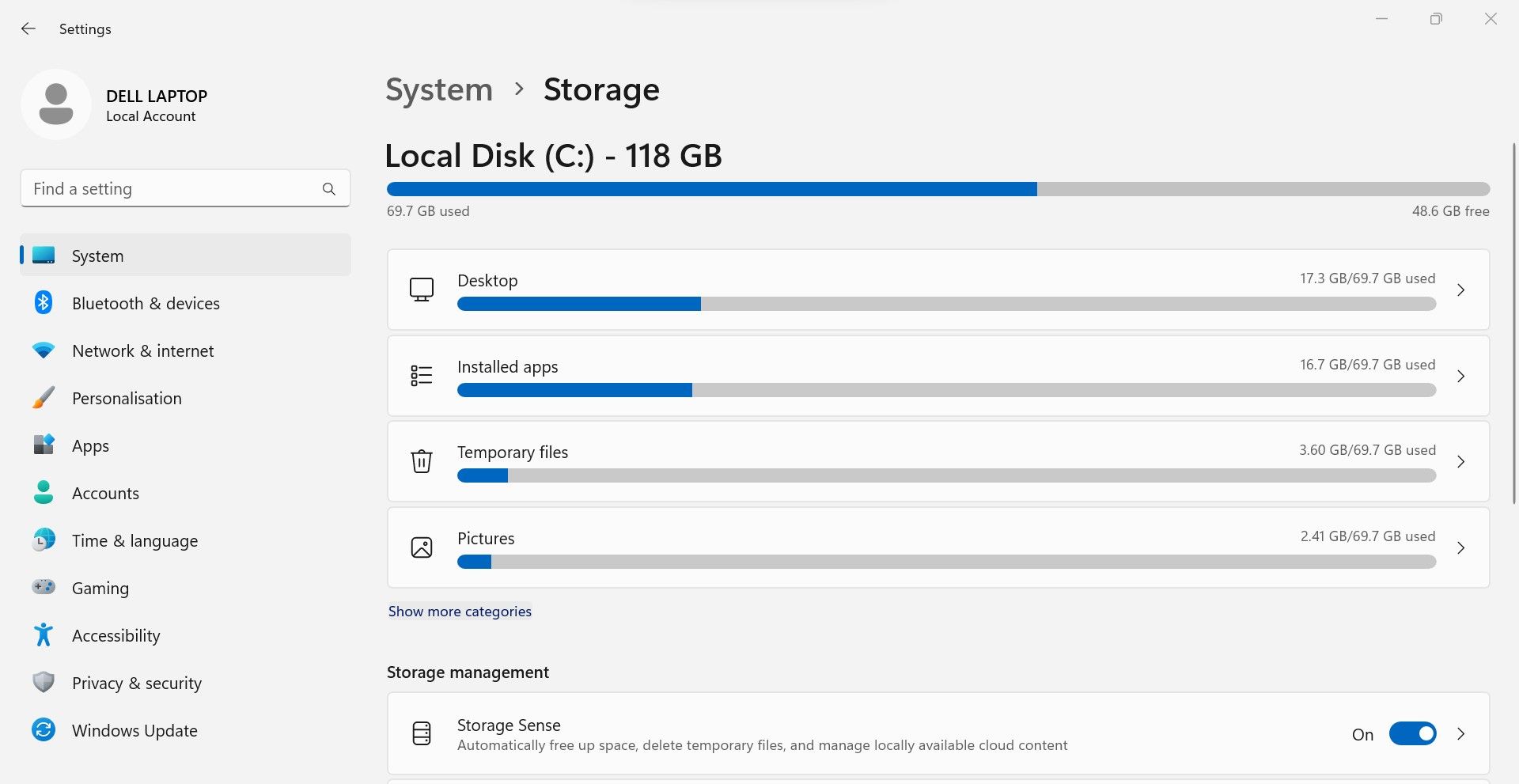


 SwifDoo PDF 2-Year Plan
SwifDoo PDF 2-Year Plan