Tackling Nonresponsive Diagnostics in Win10/Win11

Tackling Nonresponsive Diagnostics in Win10/Win11
Users often utilize the pre-installed Windows 11/10 troubleshooters available in Settings to fix update, sound, internet, microphone, video playback, Bluetooth, and UWP app issues. However, sometimes those troubleshooters display messages in their windows that say, “An error occurred while troubleshooting.” Or the message might say, “An error occurred while loading the troubleshooter.”
The full error messages and codes can vary slightly and appear after users select to run the troubleshooters. Consequently, the affected Windows troubleshooters don’t work. This is how you can fix troubleshooters not working on Windows 11/10 PCs.
1. Scan and Repair System Files
Some users have said the system file and image repair tools helped them fix Windows 11/10 troubleshooting tools not working. System File Checker is the command-line tool for repairing system file corruptions. Deployment Image Servicing and Management is a utility you can run to address issues with the Windows image. Try running both those tools in the Command Prompt, as covered within this guide for repairing corrupted Windows files .
2. Enable or Restart Required Services
Windows troubleshooters can stop working because required services are disabled or not running. Enabling and starting services like Cryptographic Services, Windows Update, BITS, and Windows Installer is a potential resolution for fixing troubleshooters users confirm to work. Try starting those required services like this:
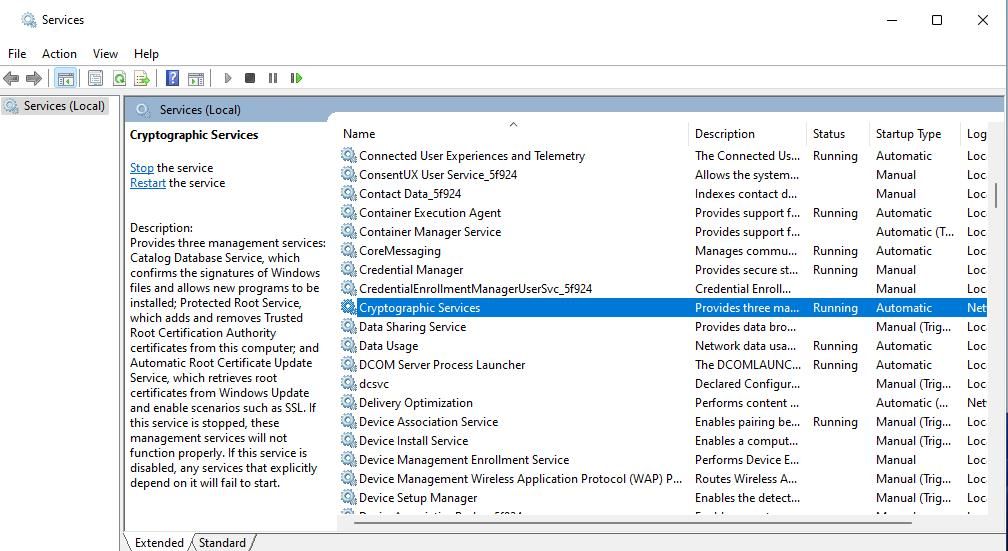
- Bring up the service management app with a method in this guide to opening Services .
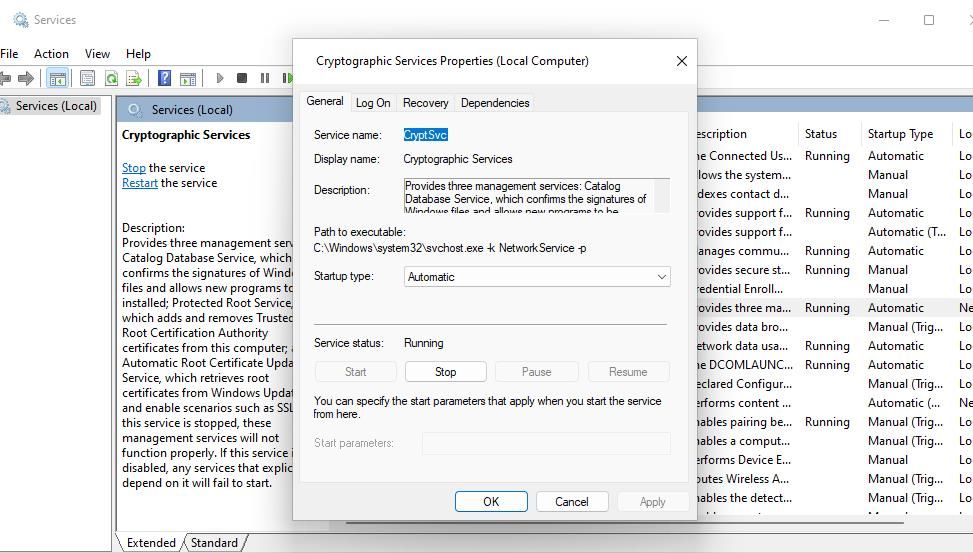
- Double-click Cryptographic Services to bring up a settings window.

- Click on the Startup type drop-down menu and choose the Automatic setting if a different option is selected.
- Next, select the Start option for the service to run.

- Click on the Apply and OK options to set your selected settings.
- Repeat the previous steps for the Windows Update, Windows Installer, and the Background Intelligent Transfer Service.
If those services are already running and set to an automatic startup, try restarting them. Right-click the service in the Services window and select a Restart option.
3. Flush the DNS Cache and Reset the Winsock Catalog
Network issues can cause some troubleshooters for which an internet connection is more essential to malfunction. Flushing the DNS cache and resetting the Winsock catalog can address such network issues. This potential fix is especially recommended for fixing the Windows Update troubleshooter. You can flush the DNS cache and reset the Winsock catalog by executing two commands like this:
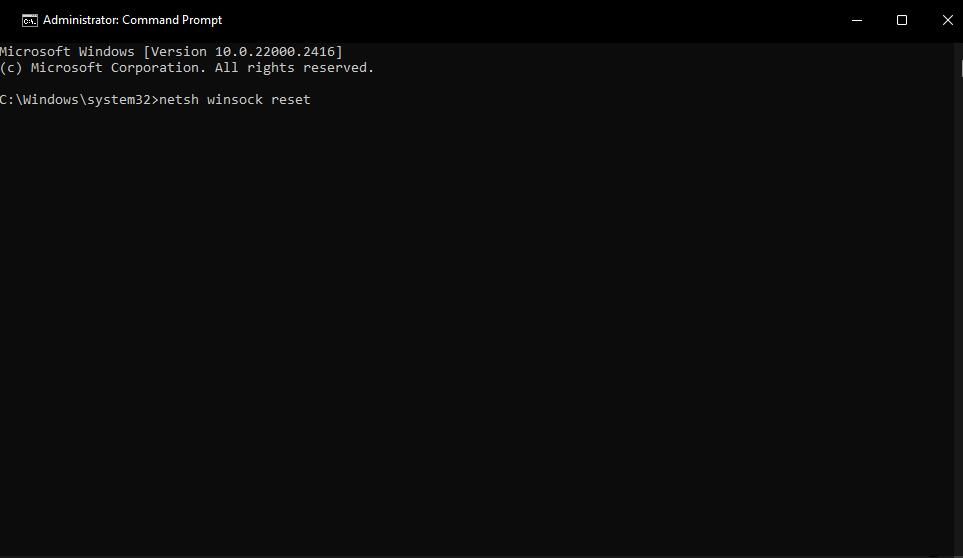
- Open the Command Prompt app with elevated privileges. If you’re unsure how to access that app, check out this guide for opening Command Prompt with admin rights .
- Input and execute this command for flushing the DNS cache:
ipconfig /flushdns
- To reset Winsock, execute this command:
netsh winsock reset
4. Disable Third-Party Security Software and Firewalls
Many security software packages incorporate firewalls that can sometimes block Windows troubleshooters from connecting with Microsoft servers. If a third-party security app is on your PC, disable that software’s firewall component to ensure it can’t interfere with Windows troubleshooters. Then try running the troubleshooter with the firewall component disabled.
5. Rename the Catroot2 and SoftwareDistribution Folders
If you’re having issues with the Windows Update troubleshooter, try applying this potential solution. Users confirm renaming the catroot2 and SoftwareDistribution folders can fix the Windows Update troubleshooter not working. Those are folders that store data for Windows updates. Rename the catroot2 and SoftwareDistribution folders as follows:
- Launch the Windows Command Prompt app with administrative rights.
- Input these four separate commands, pressing Enter after each, to stop update services:
`net stop cryptsvc
net stop wuauserv
net stop bits
net stop msiserver3. Next, input this command and hit **Return** to rename the SoftwareDistribution folder: ren c:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution SoftwareDistribution.old`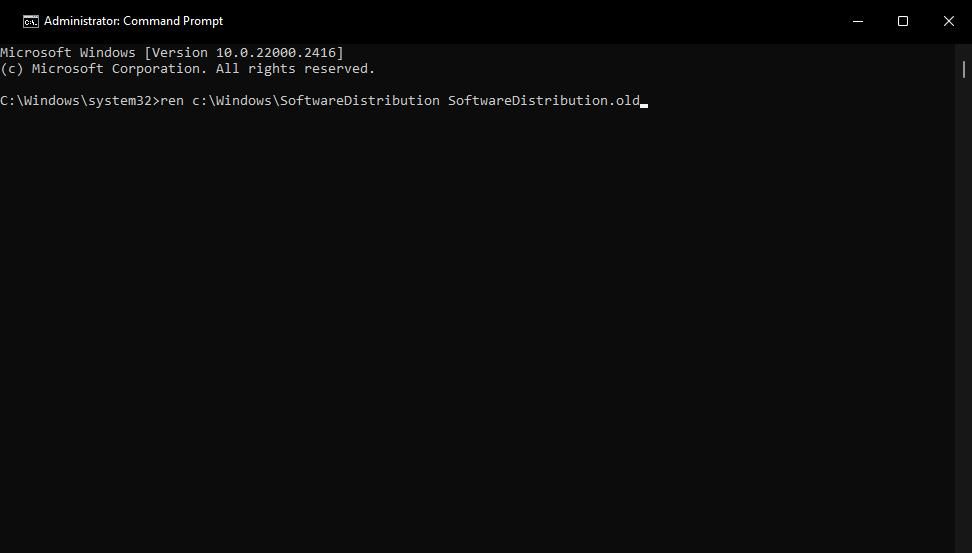
4. Enter this command for renaming the catroot2 folder and press Return:
ren c:\Windows\System32\catroot2 catroot2.old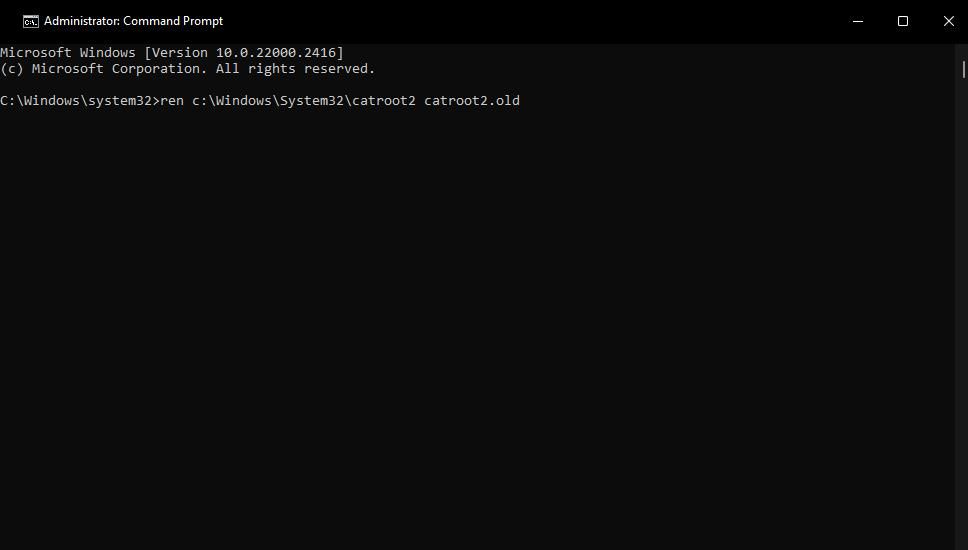
5. Restart services by entering and executing these commands:
`net start cryptsvc
net start wuauserv
net start bits
net start msiserver`
6. Modify TEMP and TMP Environment Variables
Troubleshooter issues can also arise when the TEMP and TMP environment variables have been changed from their default values. To address this, set the TMP and TEMP environment variables to default values as follows:
Open the file finder by pressing the Windows key + S keyboard buttons.
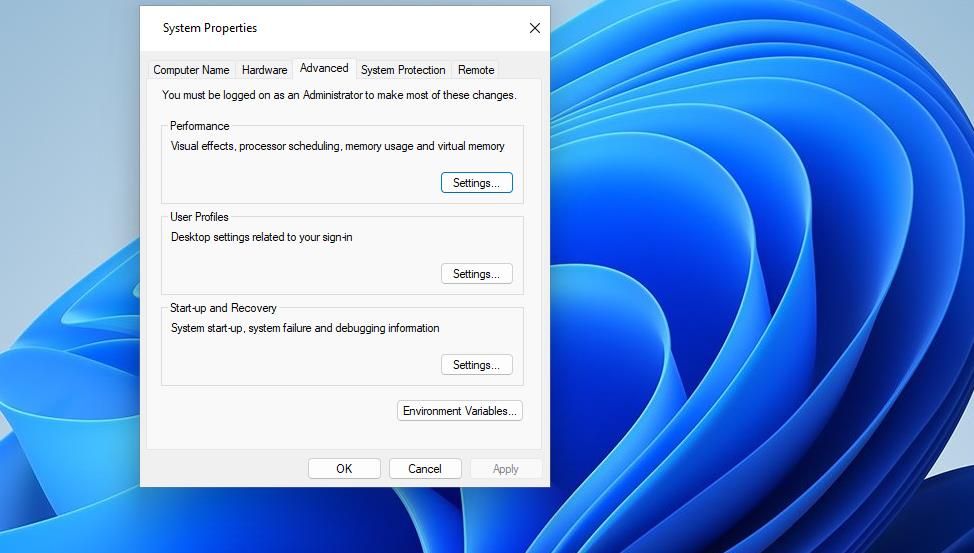
Type advanced system settings inside the search box.
Click View advanced system settings to bring up a System Properties window.
Press the Environment Variables button on the Advanced tab.

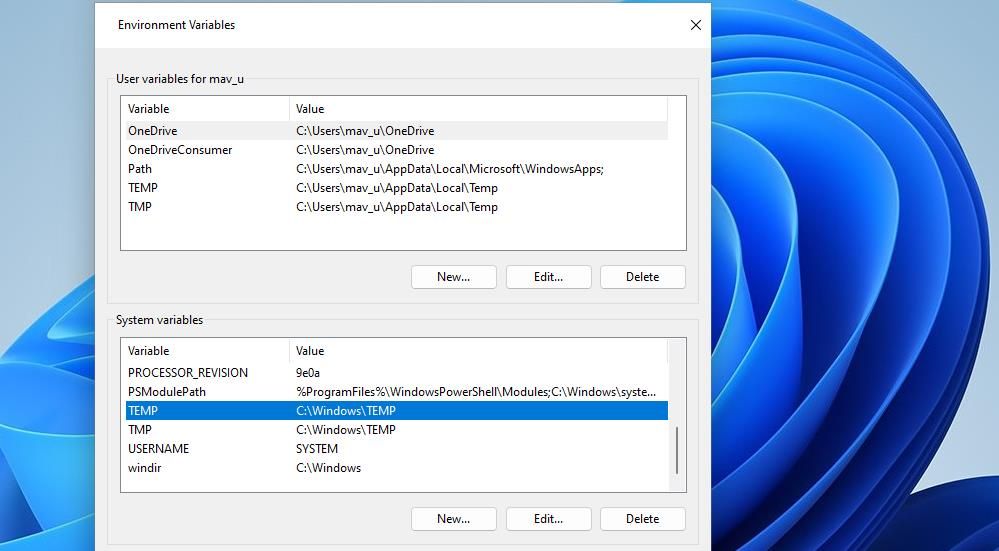
Check the TEMP and TMP values in the System variables box. If they’re not set to C:\Windows\Temp, proceed with the next few steps to edit their values.

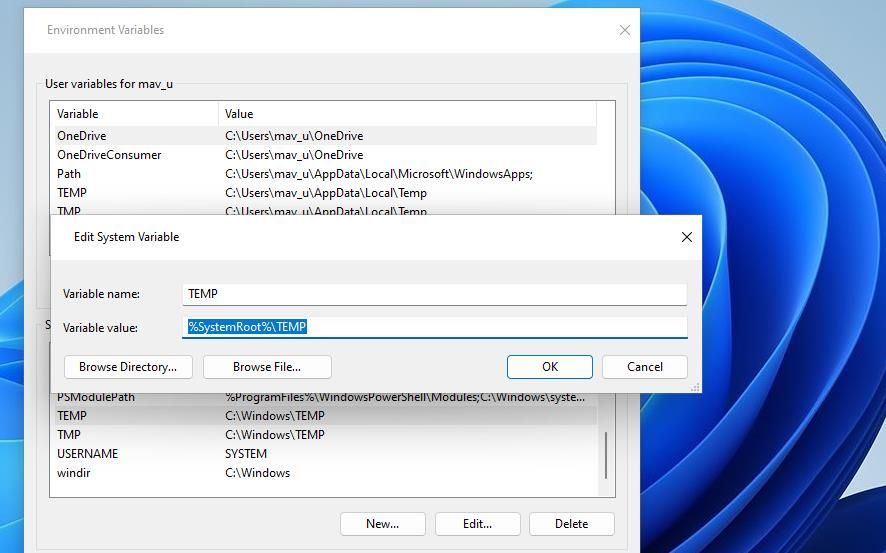
Double-click TEMP in the System variables box.
Erase the text in the Variable value box. Then input %SystemRoot%\TEMP inside the Variable value box.

Click OK on the Edit System Variable window.
Repeat the previous three steps for the TMP variable.
Select OK on the Environment Variables window.
7. Enable Troubleshooters in Group Policy Editor
Local Group Policy Editor includes policy options for disabling the Windows troubleshooters. If you’re a Windows 11/10 Pro or Enterprise user, it could be the case Group Policy has disabled the troubleshooters. That’s especially likely if the error message says troubleshooting is disabled. You can enable troubleshooting in Group Policy Editor like this:
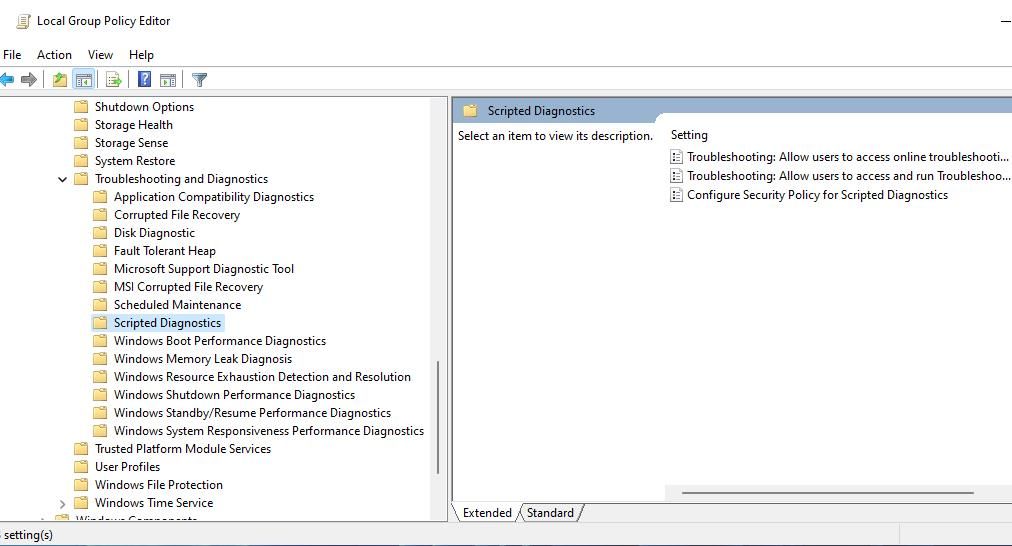
- Open Local Group Policy Editor and double-click Computer Configuration in that utility.
- Then double-click Administrative Templates > System > Troubleshooting and Diagnostics > Scripted Diagnostics to view policy settings for troubleshooting.

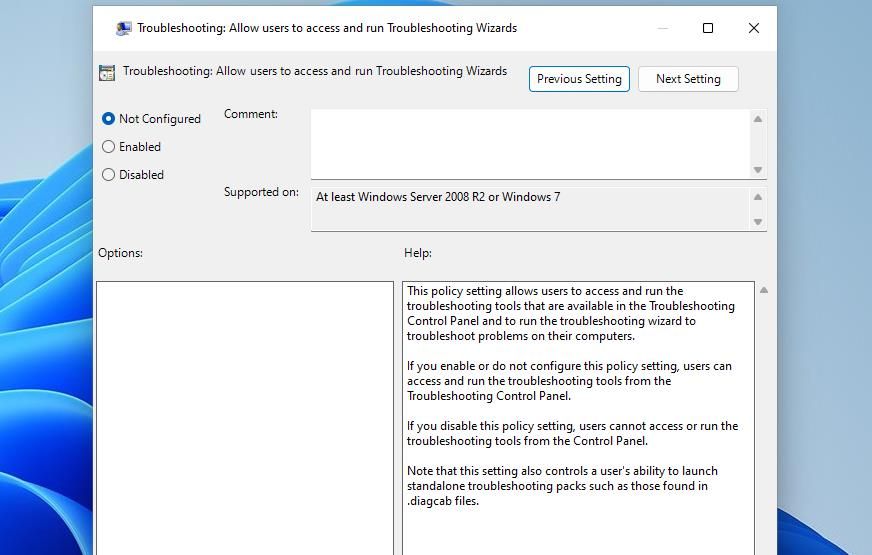
- Double-click the Troubleshooting: Allow users to access and run Troubleshooting Wizards policy.
- Click Enabled to re-enable troubleshooters if the policy is disabled.

- Press the Apply > OK buttons.
- Repeat the previous three steps for the Troubleshooting: Allow users to access online troubleshooting content and Configure Security Policy for Scripted Diagnostics policies.
8. Utilize the System Restore Tool
System Restore is a utility that undoes system changes by rolling Windows back to earlier times. This tool might undo some changes that caused the troubleshooter error. A lot depends on whether you can select a restore point that will roll Windows back to a time when you could utilize all troubleshooters without issues.
Check out this how to utilize System Restore article for instructions about how you can roll back Windows with that tool. Select a restore point that will roll Windows back to a date when all troubleshooters worked on your PC. The oldest restore point available is your best bet if you’re not sure.
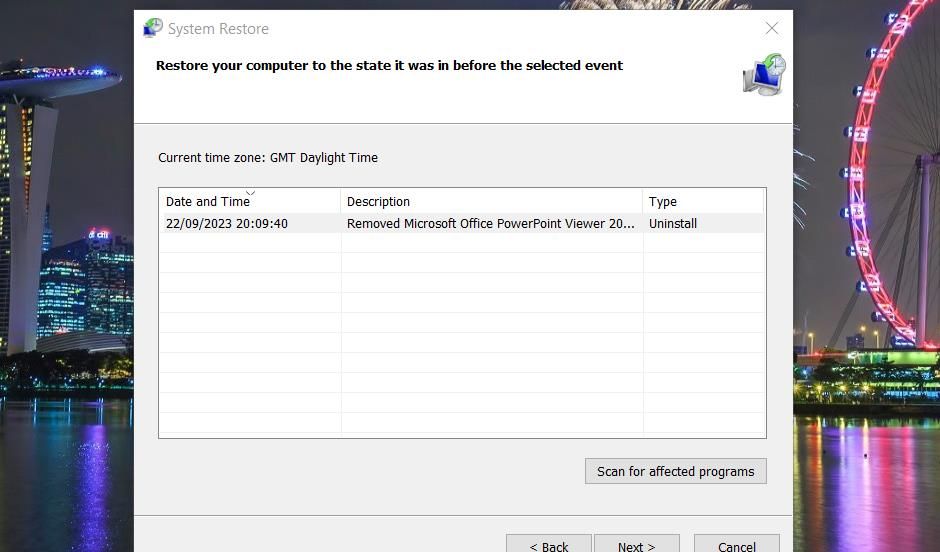
Utilizing System Restore comes with this caveat: software installed after a restoration date gets removed. This means you may need to reinstall some lost software after performing a restore. Clicking Scan for affected programs in System Restore shows you what software a restore point deleted.
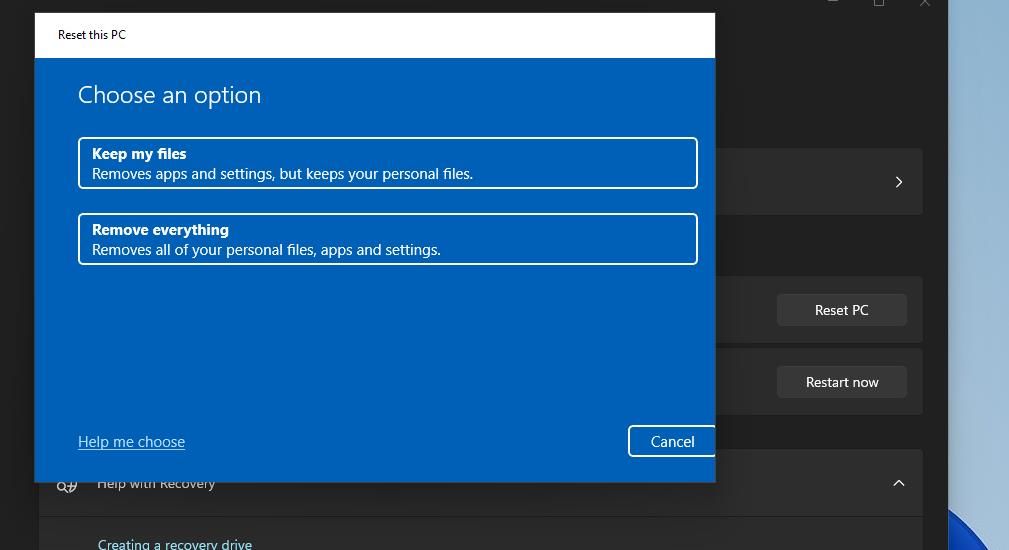
9. Factory Reset Your Windows PC
If troubleshooters still don’t work after applying all the resolutions above, resetting Windows is the last thing you should try. That might seem drastic for fixing troubleshooters, but reinstalling Windows with a reset will likely resolve deeper system issues that have broken them. This potential resolution will wipe all the software and apps you installed.
The best way to apply this potential resolution is to utilize the “Reset this PC” tool, as outlined in our article about how to factory reset Windows . Selecting Keep my files in that tool will save your user files. Also, keep the Restore preinstalled apps option set to Yes to retain preinstalled software.
Fix Your Windows Issues With the Troubleshooters Once More
Although most users can probably live without Windows troubleshooters, there’s no denying their usefulness for fixing computing issues. The potential resolutions above will likely resolve most errors that prevent Windows troubleshooters from initiating their troubleshooting. Then you can utilize the troubleshooters to help you fix Windows 10 or 11 issues again.
The full error messages and codes can vary slightly and appear after users select to run the troubleshooters. Consequently, the affected Windows troubleshooters don’t work. This is how you can fix troubleshooters not working on Windows 11/10 PCs.
Also read:
- [Updated] In 2024, IPhone Users' Ultimate Podcast Download Techniques
- [Updated] Thumbnail Magic A Filmmaker's Mobile Techniques for YouTube
- 2024 Approved Leading Virtual Reality Enhancements for Gamers
- 2024 Approved Premium Choices for Unparalleled Video Communication
- Comparing iPhones: 14 Pro and 14 Pro Max – Choose Your Next Smartphone Upgrade!
- Diagnosing Windows Alt Key Errors (48 Characters)
- Efficient Shutdown: The Guide to Auto Mode with Windows 10/11
- Efficient Techniques for YouTube Shorts Revenue for 2024
- Explore #1-#6 GPU Power Tools to Assess on Your PC
- Fixed: Installing and Troubleshooting the Intel HD Graphics nVIDIA Drivers on Microsoft Windows Platforms
- Guide to Controlling Installer Service in Windows
- Steps to Disable Protected App Ban on Windows
- Understanding the Truth About Lossless Sound Quality in Today's Earphones - Unveiling the Facts on ZDNet
- Unleash Potential Using Cookiebot's Powerful Marketing Tools
- Unraveling Disruptions: Preventing Unexpected Crashes in Dwarf Fortress
- Title: Tackling Nonresponsive Diagnostics in Win10/Win11
- Author: David
- Created at : 2025-01-15 10:34:25
- Updated at : 2025-01-18 16:08:39
- Link: https://win11.techidaily.com/tackling-nonresponsive-diagnostics-in-win10win11/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.