Rekindling File Explorer: Windows 10 Edition

Rekindling File Explorer: Windows 10 Edition
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
Quick Links
- What Is File Explorer in Windows?
- Restart File Explorer Using Task Manager
- Exit Explorer and Manually Restart It (Windows 10 Only)
- Restart Windows Explorer Manually Using Command Prompt
- Use a Batch File to Restart File Explorer in Windows
When you’re facing issues with the Windows user interface—for example, your taskbar isn’t responding or file navigation seems slow—restarting the File Explorer process can often fix the issue. We’ll show you how to do it.
What Is File Explorer in Windows?
File Explorer is the built-in file manager for Windows devices. You use it to navigate through various directories and browse for files within the operating system. It starts running in the background as soon as your computer boots up.
If you’re someone who switched from a Mac, think of File Explorer as Microsoft’s equivalent of Finder in macOS. You can open a new File Explorer window by simply clicking the folder icon in the taskbar.
Besides file management, the process behind this tool also allows you to interact with the Start menu, desktop, and taskbar items. Thus, when you restart File Explorer, you’re hitting the reboot button for most of Windows’ graphical user interface—without having to shut down or restart your PC.
1. Restart File Explorer Using Task Manager
Task Manager is a built-in system monitor that lets you start or end a process on your computer. These processes can be active programs, services, and other tasks that run in the background while you use your PC. Many people use Task Manager to monitor RAM, GPU, and CPU usage on Windows .
Since File Explorer is a process that always runs in the background, using Task Manager to restart it is a natural option. Here’s what you need to do:
- Right-click anywhere that’s empty on the taskbar and select Task Manager from the context menu to get started. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard.
- If you don’t see the following window and get the simple view instead on Windows 10, click More details.
- Next, scroll through the list of active processes and find Windows Explorer. Clicking the Name header to sort in ABC order can help here.
- Select Windows Explorer and click Restart (or Restart task on Windows 11).
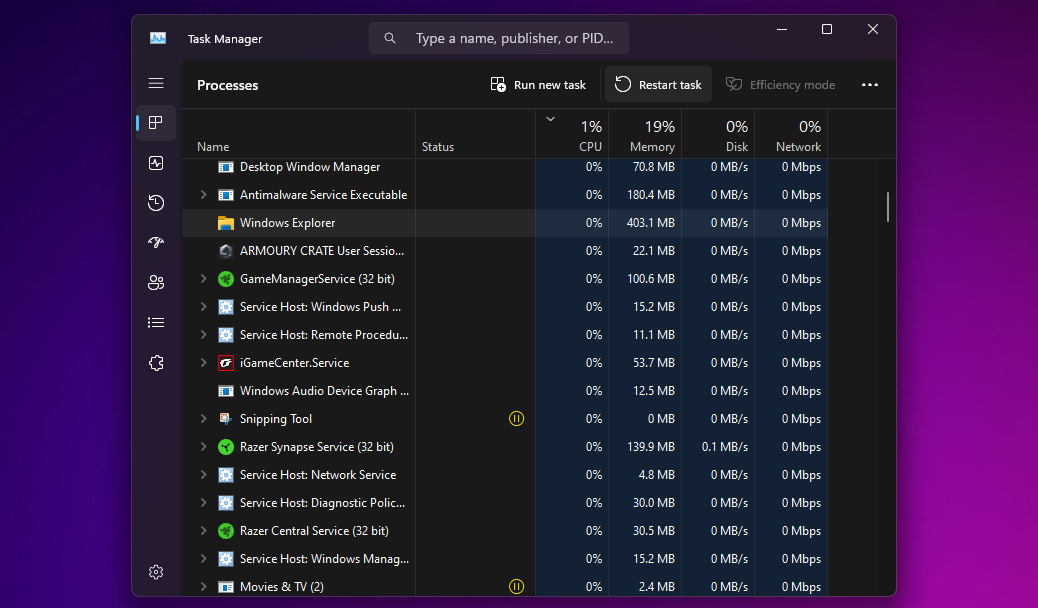
Your desktop will go black, and the taskbar will disappear for a split second, confirming that the Windows Explorer process has rebooted on your system. After the restart, the interface will likely feel more responsive; any slowdowns should be fixed.
2. Exit Explorer and Manually Restart It (Windows 10 Only)
Do you like to have more control when you restart File Explorer? Maybe you don’t want to immediately restart it because you’re testing something on your computer and need it to use as few resources as possible.
If so, Windows 10 lets you exit File Explorer, then you can manually restart it using Task Manager. Follow these steps:
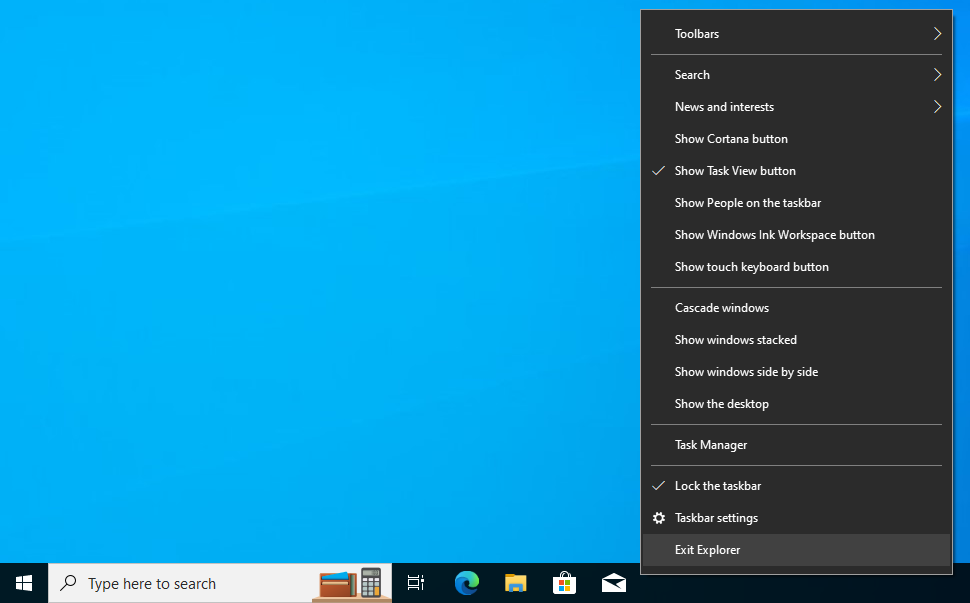
- Press Ctrl + Shift on your keyboard and right-click anywhere on the taskbar.
- Choose Exit Explorer from the context menu. Your screen will go black, and the taskbar will disappear indefinitely, but don’t panic.
- Now, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open the Task Manager.
- Go to File > Run new task from the Task Manager’s menu bar.
- You’ll be prompted to enter the name of the process you want to run. Type explorer.exe and click OK.
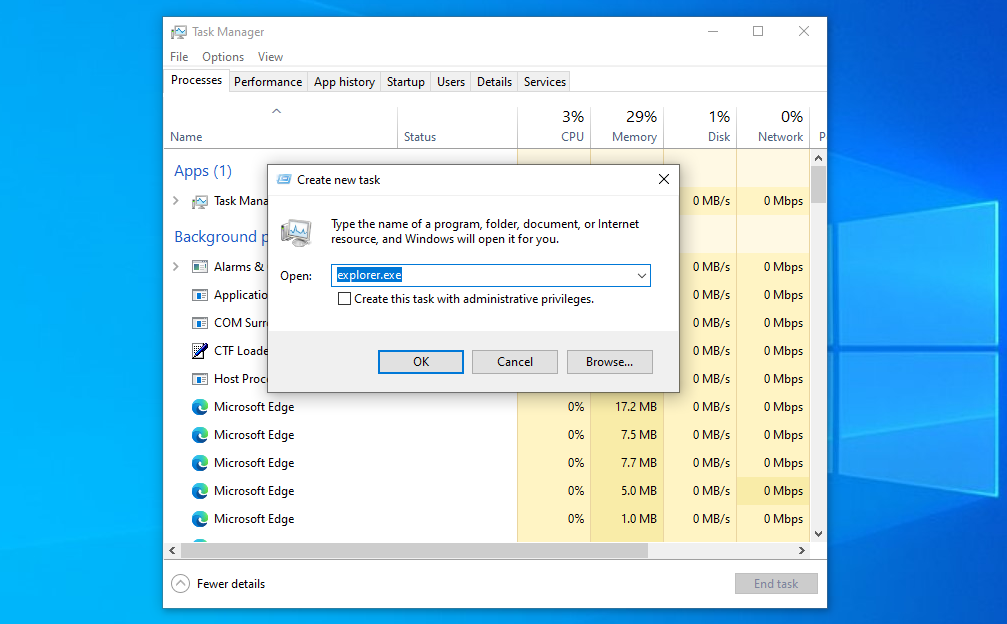
The taskbar and your desktop will reappear on the screen, confirming that File Explorer is once again actively running in the background of your system.
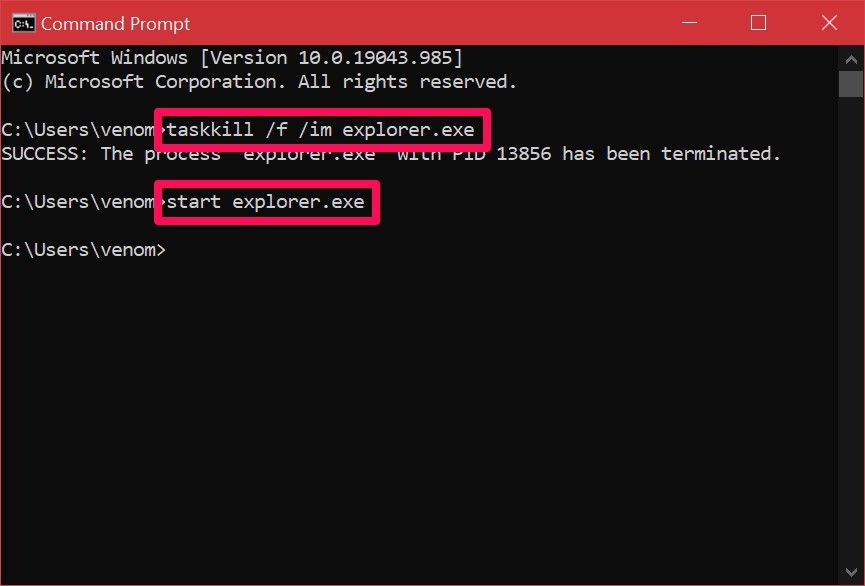
3. Restart Windows Explorer Manually Using Command Prompt
The Command Prompt is a tool that most Windows users are familiar with. This built-in command-line interpreter lets you perform various tasks on a Windows computer using specific commands.
We’ll use two separate commands to kill the Explorer.exe process and start it back up in this method. This manual method to restart File Explorer can be handy for Windows 11 users, since the above doesn’t work on the newer OS.
- Type command prompt in the Start menu search bar and open it. To stop File Explorer from running, type the following command and hit Enter:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe - When you’re ready to re-run it, use this command and press Enter:
start explorer.exe
After entering the first command, your screen will go black. You’ll be able to access your desktop again once you enter the second command.
4. Use a Batch File to Restart File Explorer in Windows
A batch file is simply a plain text file containing a series of commands you can execute with command-line interpreters like Command Prompt or PowerShell. These files use the .bat format; you can access them using File Explorer.
All the commands stored in a Windows batch file will execute automatically in sequential order once you open it. We’ll use the same two commands we used in the Command Prompt method, except you’ll store it as a batch file on your desktop for easy access:
- Use the Start menu search bar to find and open Notepad. Now, copy/paste or type the following lines:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe start explorer.exe exit - Click File > Save As from Notepad’s menu bar.
- Set the Save as type to All Files and add .bat at the end of the file name. Select a location you can quickly access, like the Desktop folder, and click Save. This will save the Notepad document as a batch file.
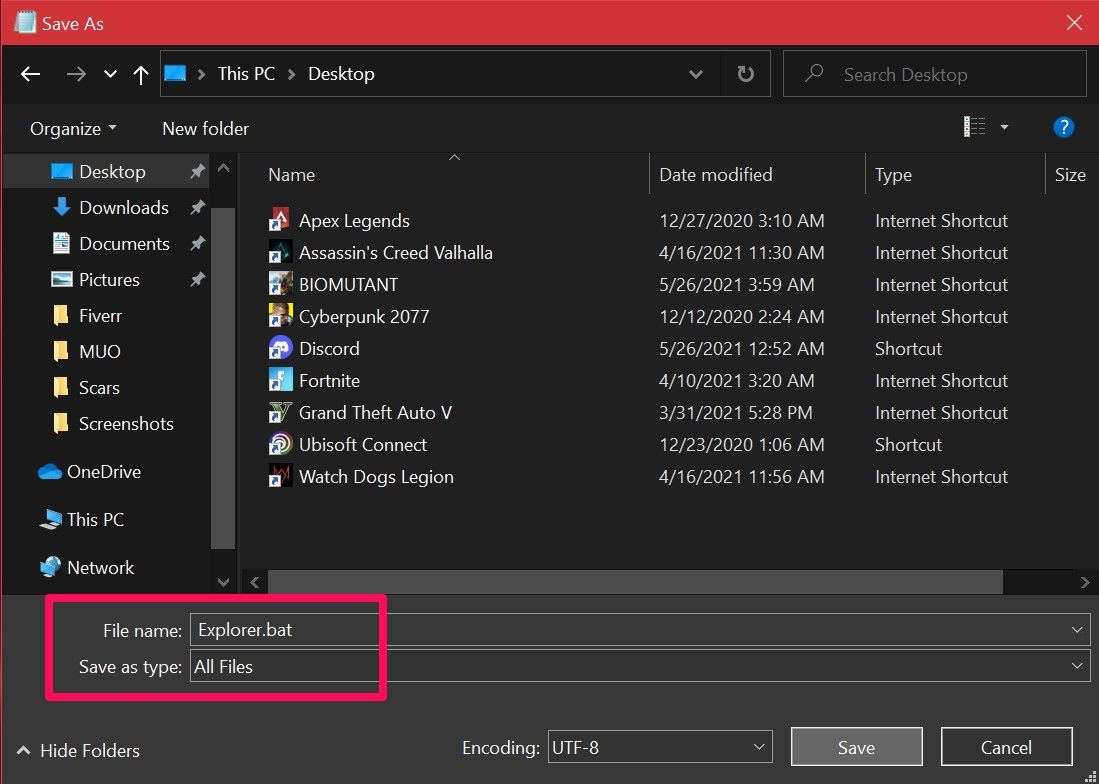
All you need to do now is double-click the file to run the commands automatically. When File Explorer restarts, your screen will go black for a moment. If you store the batch file on your desktop or pin the file to your Windows taskbar , where it’s easily accessible, this becomes the fastest way to restart Explorer.exe on your Windows PC.
Now that you’ve learned not one, but four, different ways to restart File Explorer, it’s time to figure out what works best for you. We have a clear winner if you’re looking for the fastest method. But if you don’t want to set up a batch file for the job, using Task Manager is generally your best bet.
When you’re facing issues with the Windows user interface—for example, your taskbar isn’t responding or file navigation seems slow—restarting the File Explorer process can often fix the issue. We’ll show you how to do it.
What Is File Explorer in Windows?
File Explorer is the built-in file manager for Windows devices. You use it to navigate through various directories and browse for files within the operating system. It starts running in the background as soon as your computer boots up.
If you’re someone who switched from a Mac, think of File Explorer as Microsoft’s equivalent of Finder in macOS. You can open a new File Explorer window by simply clicking the folder icon in the taskbar.
Besides file management, the process behind this tool also allows you to interact with the Start menu, desktop, and taskbar items. Thus, when you restart File Explorer, you’re hitting the reboot button for most of Windows’ graphical user interface—without having to shut down or restart your PC.
1. Restart File Explorer Using Task Manager
Task Manager is a built-in system monitor that lets you start or end a process on your computer. These processes can be active programs, services, and other tasks that run in the background while you use your PC. Many people use Task Manager to monitor RAM, GPU, and CPU usage on Windows .
Since File Explorer is a process that always runs in the background, using Task Manager to restart it is a natural option. Here’s what you need to do:
- Right-click anywhere that’s empty on the taskbar and select Task Manager from the context menu to get started. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard.
- If you don’t see the following window and get the simple view instead on Windows 10, click More details.
- Next, scroll through the list of active processes and find Windows Explorer. Clicking the Name header to sort in ABC order can help here.
- Select Windows Explorer and click Restart (or Restart task on Windows 11).

Your desktop will go black, and the taskbar will disappear for a split second, confirming that the Windows Explorer process has rebooted on your system. After the restart, the interface will likely feel more responsive; any slowdowns should be fixed.
2. Exit Explorer and Manually Restart It (Windows 10 Only)
Do you like to have more control when you restart File Explorer? Maybe you don’t want to immediately restart it because you’re testing something on your computer and need it to use as few resources as possible.
If so, Windows 10 lets you exit File Explorer, then you can manually restart it using Task Manager. Follow these steps:

- Press Ctrl + Shift on your keyboard and right-click anywhere on the taskbar.
- Choose Exit Explorer from the context menu. Your screen will go black, and the taskbar will disappear indefinitely, but don’t panic.
- Now, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open the Task Manager.
- Go to File > Run new task from the Task Manager’s menu bar.
- You’ll be prompted to enter the name of the process you want to run. Type explorer.exe and click OK.

The taskbar and your desktop will reappear on the screen, confirming that File Explorer is once again actively running in the background of your system.
3. Restart Windows Explorer Manually Using Command Prompt
The Command Prompt is a tool that most Windows users are familiar with. This built-in command-line interpreter lets you perform various tasks on a Windows computer using specific commands.
We’ll use two separate commands to kill the Explorer.exe process and start it back up in this method. This manual method to restart File Explorer can be handy for Windows 11 users, since the above doesn’t work on the newer OS.
- Type command prompt in the Start menu search bar and open it. To stop File Explorer from running, type the following command and hit Enter:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe - When you’re ready to re-run it, use this command and press Enter:
start explorer.exe
After entering the first command, your screen will go black. You’ll be able to access your desktop again once you enter the second command.
4. Use a Batch File to Restart File Explorer in Windows
A batch file is simply a plain text file containing a series of commands you can execute with command-line interpreters like Command Prompt or PowerShell. These files use the .bat format; you can access them using File Explorer.
All the commands stored in a Windows batch file will execute automatically in sequential order once you open it. We’ll use the same two commands we used in the Command Prompt method, except you’ll store it as a batch file on your desktop for easy access:
- Use the Start menu search bar to find and open Notepad. Now, copy/paste or type the following lines:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe start explorer.exe exit - Click File > Save As from Notepad’s menu bar.
- Set the Save as type to All Files and add .bat at the end of the file name. Select a location you can quickly access, like the Desktop folder, and click Save. This will save the Notepad document as a batch file.

All you need to do now is double-click the file to run the commands automatically. When File Explorer restarts, your screen will go black for a moment. If you store the batch file on your desktop or pin the file to your Windows taskbar , where it’s easily accessible, this becomes the fastest way to restart Explorer.exe on your Windows PC.
Now that you’ve learned not one, but four, different ways to restart File Explorer, it’s time to figure out what works best for you. We have a clear winner if you’re looking for the fastest method. But if you don’t want to set up a batch file for the job, using Task Manager is generally your best bet.
When you’re facing issues with the Windows user interface—for example, your taskbar isn’t responding or file navigation seems slow—restarting the File Explorer process can often fix the issue. We’ll show you how to do it.
What Is File Explorer in Windows?
File Explorer is the built-in file manager for Windows devices. You use it to navigate through various directories and browse for files within the operating system. It starts running in the background as soon as your computer boots up.
If you’re someone who switched from a Mac, think of File Explorer as Microsoft’s equivalent of Finder in macOS. You can open a new File Explorer window by simply clicking the folder icon in the taskbar.
Besides file management, the process behind this tool also allows you to interact with the Start menu, desktop, and taskbar items. Thus, when you restart File Explorer, you’re hitting the reboot button for most of Windows’ graphical user interface—without having to shut down or restart your PC.
1. Restart File Explorer Using Task Manager
Task Manager is a built-in system monitor that lets you start or end a process on your computer. These processes can be active programs, services, and other tasks that run in the background while you use your PC. Many people use Task Manager to monitor RAM, GPU, and CPU usage on Windows .
Since File Explorer is a process that always runs in the background, using Task Manager to restart it is a natural option. Here’s what you need to do:
- Right-click anywhere that’s empty on the taskbar and select Task Manager from the context menu to get started. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard.
- If you don’t see the following window and get the simple view instead on Windows 10, click More details.
- Next, scroll through the list of active processes and find Windows Explorer. Clicking the Name header to sort in ABC order can help here.
- Select Windows Explorer and click Restart (or Restart task on Windows 11).

Your desktop will go black, and the taskbar will disappear for a split second, confirming that the Windows Explorer process has rebooted on your system. After the restart, the interface will likely feel more responsive; any slowdowns should be fixed.
2. Exit Explorer and Manually Restart It (Windows 10 Only)
Do you like to have more control when you restart File Explorer? Maybe you don’t want to immediately restart it because you’re testing something on your computer and need it to use as few resources as possible.
If so, Windows 10 lets you exit File Explorer, then you can manually restart it using Task Manager. Follow these steps:

- Press Ctrl + Shift on your keyboard and right-click anywhere on the taskbar.
- Choose Exit Explorer from the context menu. Your screen will go black, and the taskbar will disappear indefinitely, but don’t panic.
- Now, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open the Task Manager.
- Go to File > Run new task from the Task Manager’s menu bar.
- You’ll be prompted to enter the name of the process you want to run. Type explorer.exe and click OK.

The taskbar and your desktop will reappear on the screen, confirming that File Explorer is once again actively running in the background of your system.
3. Restart Windows Explorer Manually Using Command Prompt
The Command Prompt is a tool that most Windows users are familiar with. This built-in command-line interpreter lets you perform various tasks on a Windows computer using specific commands.
We’ll use two separate commands to kill the Explorer.exe process and start it back up in this method. This manual method to restart File Explorer can be handy for Windows 11 users, since the above doesn’t work on the newer OS.
- Type command prompt in the Start menu search bar and open it. To stop File Explorer from running, type the following command and hit Enter:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe - When you’re ready to re-run it, use this command and press Enter:
start explorer.exe
After entering the first command, your screen will go black. You’ll be able to access your desktop again once you enter the second command.
4. Use a Batch File to Restart File Explorer in Windows
A batch file is simply a plain text file containing a series of commands you can execute with command-line interpreters like Command Prompt or PowerShell. These files use the .bat format; you can access them using File Explorer.
All the commands stored in a Windows batch file will execute automatically in sequential order once you open it. We’ll use the same two commands we used in the Command Prompt method, except you’ll store it as a batch file on your desktop for easy access:
- Use the Start menu search bar to find and open Notepad. Now, copy/paste or type the following lines:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe start explorer.exe exit - Click File > Save As from Notepad’s menu bar.
- Set the Save as type to All Files and add .bat at the end of the file name. Select a location you can quickly access, like the Desktop folder, and click Save. This will save the Notepad document as a batch file.

All you need to do now is double-click the file to run the commands automatically. When File Explorer restarts, your screen will go black for a moment. If you store the batch file on your desktop or pin the file to your Windows taskbar , where it’s easily accessible, this becomes the fastest way to restart Explorer.exe on your Windows PC.
Now that you’ve learned not one, but four, different ways to restart File Explorer, it’s time to figure out what works best for you. We have a clear winner if you’re looking for the fastest method. But if you don’t want to set up a batch file for the job, using Task Manager is generally your best bet.
When you’re facing issues with the Windows user interface—for example, your taskbar isn’t responding or file navigation seems slow—restarting the File Explorer process can often fix the issue. We’ll show you how to do it.
What Is File Explorer in Windows?
File Explorer is the built-in file manager for Windows devices. You use it to navigate through various directories and browse for files within the operating system. It starts running in the background as soon as your computer boots up.
If you’re someone who switched from a Mac, think of File Explorer as Microsoft’s equivalent of Finder in macOS. You can open a new File Explorer window by simply clicking the folder icon in the taskbar.
Besides file management, the process behind this tool also allows you to interact with the Start menu, desktop, and taskbar items. Thus, when you restart File Explorer, you’re hitting the reboot button for most of Windows’ graphical user interface—without having to shut down or restart your PC.
1. Restart File Explorer Using Task Manager
Task Manager is a built-in system monitor that lets you start or end a process on your computer. These processes can be active programs, services, and other tasks that run in the background while you use your PC. Many people use Task Manager to monitor RAM, GPU, and CPU usage on Windows .
Since File Explorer is a process that always runs in the background, using Task Manager to restart it is a natural option. Here’s what you need to do:
- Right-click anywhere that’s empty on the taskbar and select Task Manager from the context menu to get started. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard.
- If you don’t see the following window and get the simple view instead on Windows 10, click More details.
- Next, scroll through the list of active processes and find Windows Explorer. Clicking the Name header to sort in ABC order can help here.
- Select Windows Explorer and click Restart (or Restart task on Windows 11).

Your desktop will go black, and the taskbar will disappear for a split second, confirming that the Windows Explorer process has rebooted on your system. After the restart, the interface will likely feel more responsive; any slowdowns should be fixed.
2. Exit Explorer and Manually Restart It (Windows 10 Only)
Do you like to have more control when you restart File Explorer? Maybe you don’t want to immediately restart it because you’re testing something on your computer and need it to use as few resources as possible.
If so, Windows 10 lets you exit File Explorer, then you can manually restart it using Task Manager. Follow these steps:

- Press Ctrl + Shift on your keyboard and right-click anywhere on the taskbar.
- Choose Exit Explorer from the context menu. Your screen will go black, and the taskbar will disappear indefinitely, but don’t panic.
- Now, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open the Task Manager.
- Go to File > Run new task from the Task Manager’s menu bar.
- You’ll be prompted to enter the name of the process you want to run. Type explorer.exe and click OK.

The taskbar and your desktop will reappear on the screen, confirming that File Explorer is once again actively running in the background of your system.
3. Restart Windows Explorer Manually Using Command Prompt
The Command Prompt is a tool that most Windows users are familiar with. This built-in command-line interpreter lets you perform various tasks on a Windows computer using specific commands.
We’ll use two separate commands to kill the Explorer.exe process and start it back up in this method. This manual method to restart File Explorer can be handy for Windows 11 users, since the above doesn’t work on the newer OS.
- Type command prompt in the Start menu search bar and open it. To stop File Explorer from running, type the following command and hit Enter:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe - When you’re ready to re-run it, use this command and press Enter:
start explorer.exe
After entering the first command, your screen will go black. You’ll be able to access your desktop again once you enter the second command.
4. Use a Batch File to Restart File Explorer in Windows
A batch file is simply a plain text file containing a series of commands you can execute with command-line interpreters like Command Prompt or PowerShell. These files use the .bat format; you can access them using File Explorer.
All the commands stored in a Windows batch file will execute automatically in sequential order once you open it. We’ll use the same two commands we used in the Command Prompt method, except you’ll store it as a batch file on your desktop for easy access:
- Use the Start menu search bar to find and open Notepad. Now, copy/paste or type the following lines:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe start explorer.exe exit - Click File > Save As from Notepad’s menu bar.
- Set the Save as type to All Files and add .bat at the end of the file name. Select a location you can quickly access, like the Desktop folder, and click Save. This will save the Notepad document as a batch file.

All you need to do now is double-click the file to run the commands automatically. When File Explorer restarts, your screen will go black for a moment. If you store the batch file on your desktop or pin the file to your Windows taskbar , where it’s easily accessible, this becomes the fastest way to restart Explorer.exe on your Windows PC.
Now that you’ve learned not one, but four, different ways to restart File Explorer, it’s time to figure out what works best for you. We have a clear winner if you’re looking for the fastest method. But if you don’t want to set up a batch file for the job, using Task Manager is generally your best bet.
Also read:
- [New] The Beginner's Guide to LUTs and Downloading Tools for 2024
- [Updated] Android Non-Root Audio Capture 4 Easy Methods for 2024
- [Updated] IPhone Sound Capturing 101 – Voice Memo Processing for 2024
- Conquer Windows 10 Blues: A Fix-It Manual
- Cutting Through Frozen Windows Update Snags Quickly
- Dive Into the Past with Your Camera Roll and Snapchat
- Effortless Guide: How to Enjoy Japanese Film DVDs in America Regardless of Regional Lockout Constraints
- In 2024, Top-Quality Video Summaries with Smart Templates
- Mastering Projector Screens Without PIN in Win11
- New Era of Connectivity: Windows for iPhones, iPads and PCs Just Dropped!
- Reversing Missing Directory Indicators
- Spiral Fabricator Package for 2024
- Step-by-Step Guide: Crafting Compelling Facebook Cover Videos for Maximum Impact
- Steps to Secure Sticky Notes on Modern OSes
- The Ultimate Guide to iPad Add-Ons for a Superior Experience - Expert Reviews
- Turbocharging Your PC's Download Speed with Steam
- Unveiling Driver Verifier Within Win11 Control Panel
- Title: Rekindling File Explorer: Windows 10 Edition
- Author: David
- Created at : 2024-10-14 16:01:11
- Updated at : 2024-10-15 20:18:03
- Link: https://win11.techidaily.com/rekindling-file-explorer-windows-10-edition/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.