Escalating Network Capacity: Bypassing Windows' Setbacks at 100Mbps

Escalating Network Capacity: Bypassing Windows’ Setbacks at 100Mbps
Is the speed of your Ethernet connection stuck at 100Mbps? If so, several factors could be limiting it. You may only have a 100Mbps connection, and the speed technically cannot go higher; router settings could be limiting the bandwidth, or there could be an issue with the router, Ethernet cable, or cable connectors.
Likewise, misconfigured Ethernet adapter speed settings, incompatible or corrupted drivers, and technical difficulties with the ISP can also limit speed. If you want your Ethernet connection to surpass 100Mbps, here are a few checks and fixes you should try.
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
1. Check Your Internet Plan

Make sure you have a high-speed connection capable of delivering speeds greater than 100Mbps before you blame other factors for limiting your internet speed. Check with your internet provider that you’re subscribed to a plan that offers 100Mbps+ or more. Also, ensure the ISP has a good reputation and track record of consistently delivering high speeds.
If your internet service provider is reliable and you are subscribed to a good plan, then it’s likely that something on your side is keeping the speed from reaching its maximum.
2. Perform Some Basic Checks
Start troubleshooting the problem by performing these basic fixes, as they may resolve the issue right away:
- Reboot your router once to rule out temporary issues.
- Ensure the Ethernet cable isn’t loosely connected to your device. Disconnect both ends of the cable and reconnect them.
- Run the built-in network troubleshooter to identify and resolve any network problems. If you’re not familiar with the process, check out our guide on how to run a troubleshooter .
- An outdated network driver can also slow down a connection. Check out our guide on how to find and replace outdated network drivers to update your network drivers fully.
If none of the above checks uncaps the internet speed, it’s time to move on to the remaining fixes
3. Ensure Your Network Card Supports Gigabit Speed
The Ethernet Card, also known as the Network Interface Card, connects your computer to the internet via an Ethernet cable. If you have an old computer, the adapter installed may not be capable of delivering over 100Mbps. Therefore, ensuring that your card supports the gigabit connection is imperative.
To check this, look at the name of the adapter. If it contains keywords such as gigabit, gbe, 10/100/1000M gigabit, you probably have a gigabit connection. In contrast, if you see Fast Ethernet, 10/100FE, your connection is 100Mbps. Alternatively, you can check if your network adapter supports gigabit speeds in Device Manager. Here’s how:
- Right-click the Start button and select Device Manager.
- Expand the Network adapters category.
- Right-click the network connection adapter and select Properties.
- Then, go to the Advanced tab.
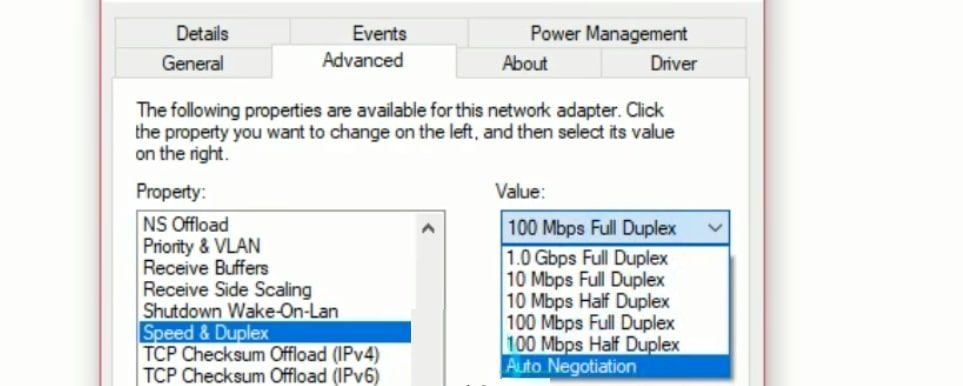
- Select Speed and Duplex from the Property column, then expand the Value dropdown.

If 1.0 Gbps Full Duplex is listed, your card supports gigabit connectivity. Your card does not support gigabit connections if 100 Mbps Full Duplex is the highest value listed. In any case, select Auto Negotiation from the Value dropdown in the network adapter settings if any other value is selected.
4. Ensure Your Router Supports Gigabit Connection

Like your network card, your router should also be capable of delivering 100Mbps+ speeds. You can check that by looking at the router’s documentation or description on the manufacturer’s website. If the router manufacturer claims this specific model is a gigabit router, it can likely deliver gigabit speeds.
If you have a gigabit router, make sure the port where your Ethernet cable is connected is also a gigabit LAN port that can handle up to 1Gbps data rates. Switch to a gigabit port if it’s connected to a “Fast Ethernet” port, which can only deliver 100Mbps. Hopefully, this will increase your internet connection’s speed.
If your router doesn’t support a gigabit connection, you will have no choice but to switch to one that does.
5. Get a High-Category Ethernet Cable

The Ethernet cable itself should be capable of delivering 100Mbps+ speed, just like your router. Ethernet cables with low bandwidth, such as Cat5, can only deliver speeds up to 100Mbps. If you want higher speeds, you need at least Cat5e cable, which can provide speeds of up to 1000Mbps.
Cat5e and Cat5 cables have identical physical appearances, but don’t let that fool you. Instead, look at the cable’s label to determine its category. If it’s low bandwidth, replace it with Cat5e or higher.
6. Remove Restrictions in the Router Settings
Most routers allow users to limit the connection speed. Therefore, log into the router’s admin interface to ensure speed isn’t constrained there. Here’s how you can do it:
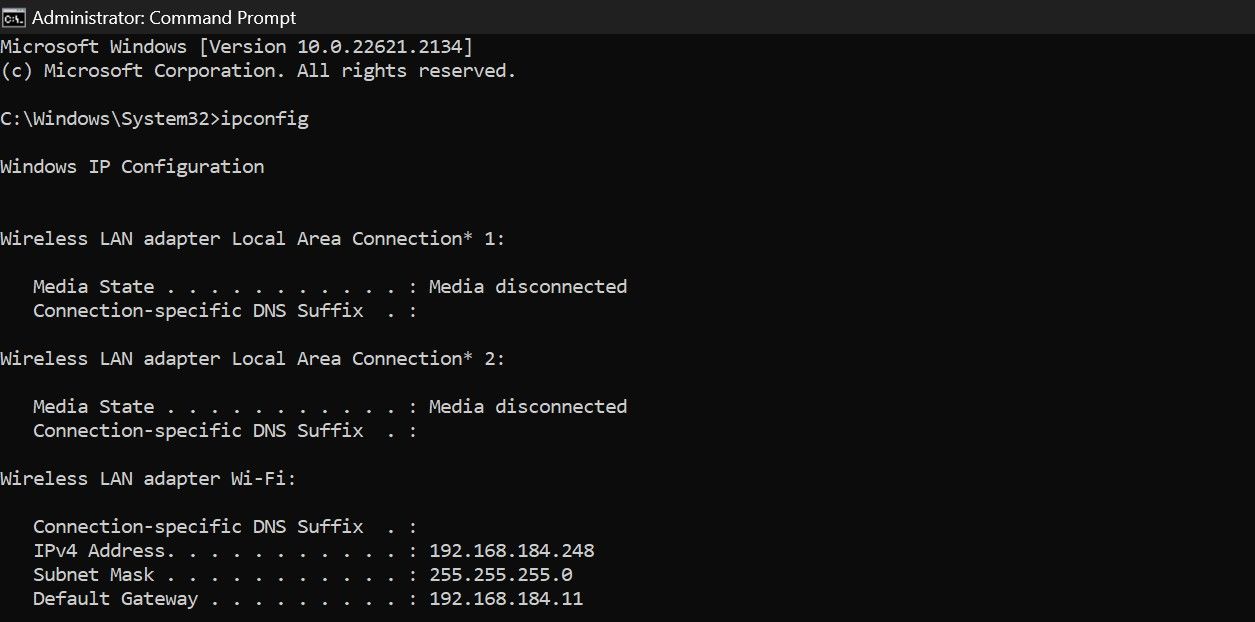
- Open the Command Prompt and type “ipconfig.” Then, hit Enter.
- Copy the IP address next to Default Gateway—that’s your router’s IP address.

- Paste this address into any internet browser to access your router’s admin interface. Then, log in with your username and password.
- Go to the Ethernet settings and check if there are any restrictions on your internet speed. Remove any constraints you find here.
Some routers allow users to switch between gigabit and 100Mbps speeds. If your router offers this option, opt for the 1Gbps connection.
7. Rule Out Any Hardware Issues
If none of the above fixes resolve the issue, it’s time to check for and rule out hardware problems thoroughly.

Start the hardware inspection by checking both ends of the Ethernet cable where cable connectors are installed. Ensure both connectors are in good condition and all internal wires/conductors are pushed to the end and aren’t falling off.
Once you have confirmed that, inspect the Ethernet cable from one end and go through the entire length. If the cable shows any physical damage, especially areas that remain bent all the time, you may need to replace it.
If the cable is intact, examine the Ethernet ports on your router and laptop. If any of the ports appears damaged, you should switch to another one (if available).
Get the Most Out of Your Ethernet Connection on Windows
Getting 100Mbps when subscribed to a higher-speed plan can be pretty frustrating. By now, you should better understand why the connection speed could be capped at 100Mbps. If you carefully follow all the steps listed above, you will likely be able to identify the leading cause and remove any restrictions.
If your internet speed remains capped at 100Mbps despite applying all the fixes above, you should contact your internet service provider.
Likewise, misconfigured Ethernet adapter speed settings, incompatible or corrupted drivers, and technical difficulties with the ISP can also limit speed. If you want your Ethernet connection to surpass 100Mbps, here are a few checks and fixes you should try.
Also read:
- [Updated] 2024 Approved Optimal Storage Expansion for Sony A7C
- [Updated] 2024 Approved Virtual PlayStation Revival on Android? Try the 5 Best Emulators Here
- [Updated] In 2024, Unveiling the Ultimate 11 Strategies for Impeccable Color Balancing
- Best Realme C51 Pattern Lock Removal Tools Remove Android Pattern Lock Without Losing Data
- Can You Unlock Apple iPhone 6s After Forgetting the Passcode?
- Enhancing Tablet Usability with Windows 11'S Taskbar
- Fixing Crackling Sound in Headphones: Fast Solutions
- How To Seamlessly Watch Apple TV Plus Shows Through Your Chromecast Device
- Improve Your Visual Output: Boosting Win 11'S VRAM
- In 2024, Tutorial Transforming Video Content Into Captivating Animated GIFS
- Mending Undetected Additional Monitor W11
- Optimal Settings Guide: Xbox App & Windows Installation
- Troubleshooting: Overcoming Chrome's Profile Glitches on PC
- Unleashing Typing Potential: Seven Windows Fixes for Lag Reduction
- Title: Escalating Network Capacity: Bypassing Windows' Setbacks at 100Mbps
- Author: David
- Created at : 2024-12-02 16:28:52
- Updated at : 2024-12-06 20:49:27
- Link: https://win11.techidaily.com/escalating-network-capacity-bypassing-windows-setbacks-at-100mbps/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.