Enhancing Memory Efficiency with Edge WebView2 Fixes

Enhancing Memory Efficiency with Edge WebView2 Fixes
Background processes can often act as hidden culprits, slowing down your computer without you knowing. When they consume more memory than they should, it’s time to take action. One such process known to cause issues is the Microsoft Edge WebView2.
In this article, we’ll look at the Microsoft Edge WebView2 process and guide you on preventing it from hogging your computer’s memory.
What Is the Microsoft Edge WebView2 Process?
The Microsoft Edge WebView2 process is a part of the Microsoft Edge web browser. Its primary function is to enhance your browsing experience within Windows applications. It’s akin to having a mini web browser attached to other Windows programs on your computer.
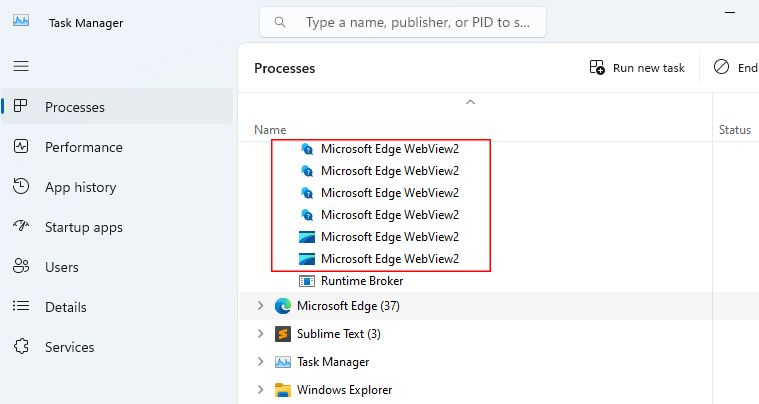
This process operates in the background, assisting Windows apps in connecting to the internet and displaying web content. This way, the apps don’t need to launch your computer’s default web browser.
For instance, consider when you’ve used any premium Windows apps that request a payment. Once you’re ready to pay, the payment gateway pops up within the app itself. There, you input your payment details and complete the transaction. This functionality is made possible due to WebView2.
However, despite its benefits, there can be times when the process consumes more memory than it should. So, let’s explore how to fix the Microsoft Edge WebView2 process memory consumption issue.
Should You Stop the Microsoft Edge WebView2 Process?
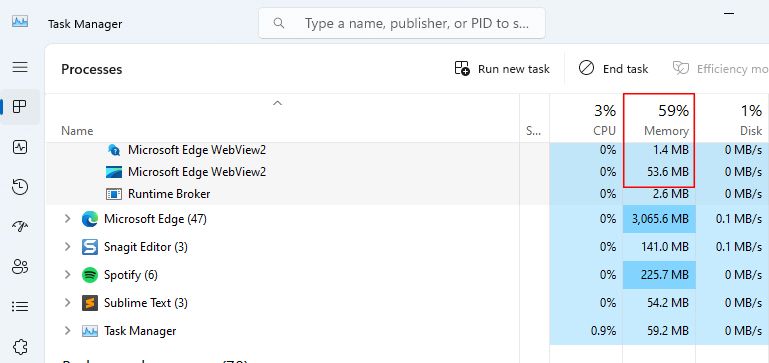
The Microsoft Edge WebView2 process should only consume a small amount of memory. If it starts eating more, it’s safe to stop it.
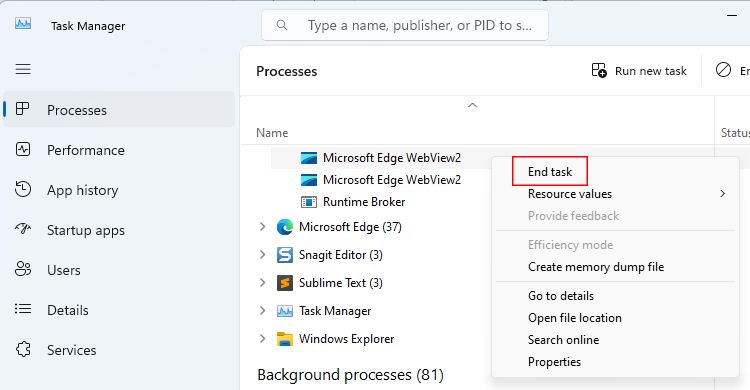
But here’s what you need to know: stopping the Microsoft Edge WebView2 process may have some downsides. For example, if you’re currently using an app like Get Help that depends on WebView2, such an app wouldn’t work correctly.
In other cases, as we’ve mentioned before, stopping the process is a wise decision. So, whether to stop the process or not, it all depends on your current use case.
How to Fix High Memory Usage From the Microsoft Edge WebView2 Process
Technically, there are only a few ways to resolve the increased memory consumption issue. Let’s check them one by one to see which one works for you.
1. Update Microsoft Edge First
As mentioned earlier, Microsoft Edge WebView2 is connected to Microsoft Edge, the default Windows browser. If WebView2 consumes a lot of memory, consider updating Microsoft Edge first.
Here are the steps to help you update to the latest Microsoft Edge version:
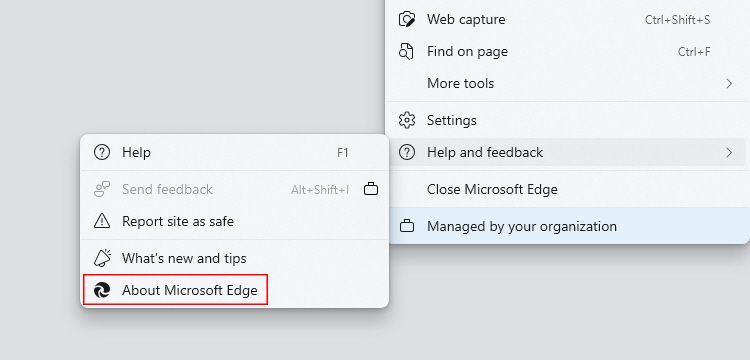
- Open Microsoft Edge and press Alt + F. If you don’t see a dropdown menu with many options, click the three-dot menu at the top right.
- Hover over the Help and feedback option in the dropdown menu. From the options, click on About Microsoft Edge.

- A new browser tab will open, and it’ll scan for any available new version updates and install them. Once the browser installs all the updates, restart Microsoft Edge.
- After updating, we recommend restarting the computer. And after a restart, open the Task Manager and check the Memory percentage status for an idea.

If you fail to update using the given steps, you can always download the updated version from Microsoft.com .
2. Reinstall Microsoft Edge WebView2
If you’re still experiencing high memory usage issues, try another approach. This time, let’s reinstall Microsoft Edge WebView2. Reinstalling WebView2 will remove all the corrupted files, if any.
Reinstalling it is as simple as installing an application. Go to the Microsoft Edge Developer’s site and download the installer file by clicking x64 or x86. Then, run the Runtime Installer file and follow the setup instructions.

3. Reset Microsoft Edge’s Settings
If reinstalling fails, your last option is to reset the Microsoft Edge settings. We know this is risky, as all your browser settings will reset. But resetting the settings can help solve any misconfigurations that might be causing excessive memory usage.
To proceed with a reset, go to Settings and click on the Reset settings option from the sidebar. Once there, click on Restore settings to their default values > Reset.
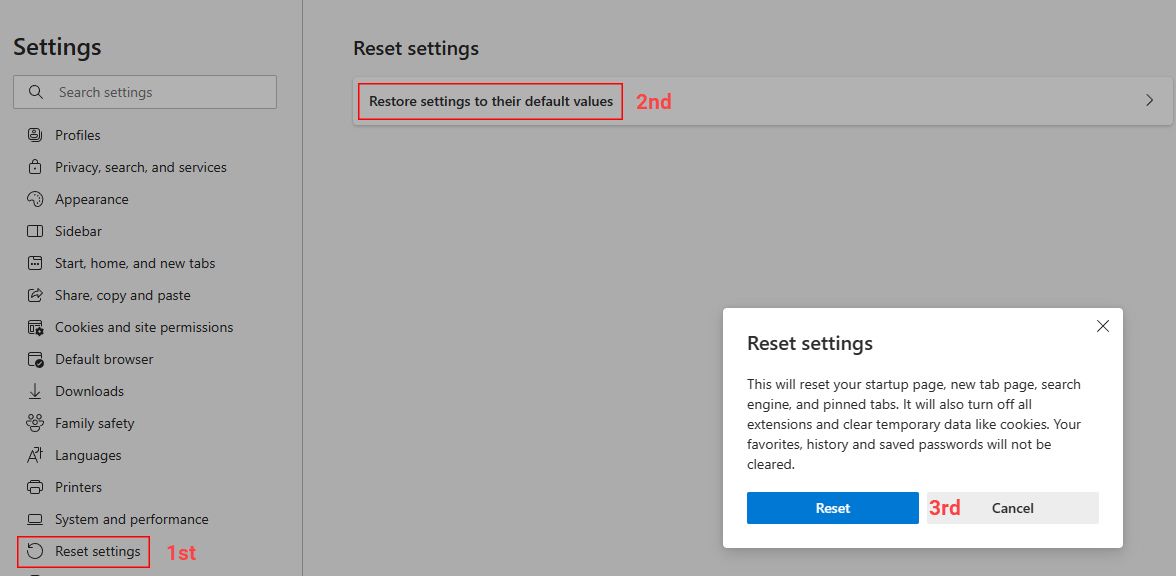
As mentioned above, resetting will remove your personalized browser settings. So, note down any specific settings you may want to change later.
Microsoft Edge WebView2’s Process Is Back to Normal
Sometimes, when we see a memory or disk usage spike, we ignore it by choice! But digging deeper and finding the main issue is wise in such situations.
The same goes for Microsoft Edge WebView2. In most cases, it helps render web content inside Windows applications. But in some rare cases, it may cause heavy lagging issues by hogging the memory.
In this article, we’ll look at the Microsoft Edge WebView2 process and guide you on preventing it from hogging your computer’s memory.
Also read:
- [New] 2024 Approved A Critical Look at Huawei P10 for Photography Enthusiasts
- [Updated] EarHearer Live Sound Critique
- [Updated] Navigate to New Horizinas Top Win11 Gaming Delights
- 五種有效的方式讓你拿回被丟棄在資源回收筒的重要文件
- In 2024, How To Simulate GPS Movement With Location Spoofer On OnePlus Ace 2 Pro? | Dr.fone
- Navigating the Seas of Application & Browser Control
- Navigating Through Windows Forbidden Errors
- Resolving Windows 11/10'S Unauthorized Access to CP
- Singing Mastery with SML385BTBK: Top Rated, No Hassle & Plug 'N Play Karaoke System
- Speed-Up Sessions: Commanding Project Mastery
- Step-by-Step Tutorial How To Bypass Honor Magic 5 FRP
- Strategies for Streaming FB Live on Zoom Platform
- Swift Solution for Faulty Windows: 0X80072AF9 Fix
- The Future of Your PC - Windows' Latest February Update Features
- The Ultimate Fix Guide for Navigating Through 'Error Code: 0X80004005'
- Trimming High CPU Usage: Vanguard's User-Mode Service Guide
- Why Most People Stick with Windows 10: Seven Reasons
- Title: Enhancing Memory Efficiency with Edge WebView2 Fixes
- Author: David
- Created at : 2024-12-01 16:28:49
- Updated at : 2024-12-07 06:36:15
- Link: https://win11.techidaily.com/enhancing-memory-efficiency-with-edge-webview2-fixes/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.